1. Introduction
Among the many types of conduit materials available, two stand out as the most commonly used: PVC conduit and steel conduit.
One of the first questions you might ask is: “Should I use PVC conduit or steel conduit?”
It’s a common dilemma because both materials offer distinct advantages and disadvantages depending on the application.
In this post, we’ll provide a clear and detailed comparison between these two popular conduit types.
We’ll cover everything from their material characteristics and the key industry standards they comply with, to practical considerations like installation ease, costs, and upkeep.
Additionally, we’ll examine how PVC and steel conduits hold up in different environmental conditions, helping you make the best choice for your project.
Whether you’re an electrical contractor, engineer, project manager, or anyone involved in electrical work, this guide maybe helpful for understanding the differences between PVC conduit and steel conduit.
Let’s get started!
To begin, we’ll focus on the materials being used and how they perform in terms of strength, flexibility, and other mechanical properties.
2. PVC Conduit and Steel Conduit: Material and Physical Properties
PVC and steel conduits are made from very different materials, and those differences shape how each performs in the field—from installation and safety to how they age over time.
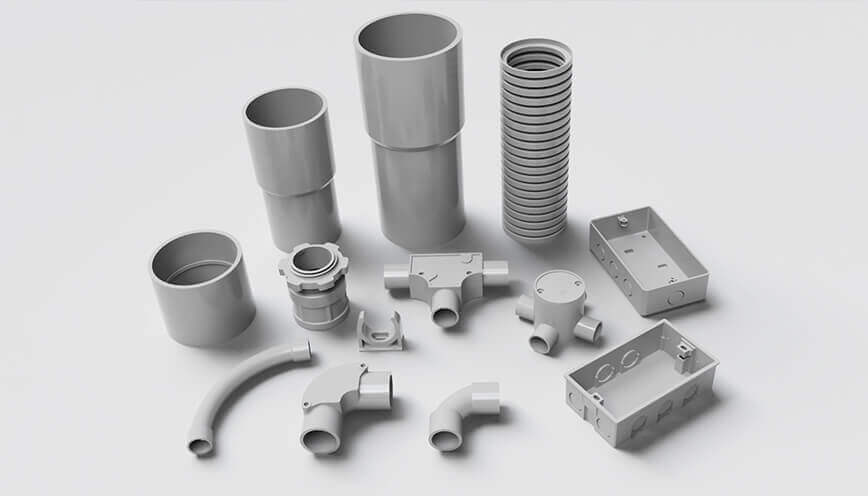
Interestingly, despite their material contrast, both PVC and steel conduits come in two main types:
Rigid conduit, used for fixed, straight runs where protection and stability are essential;
Flexible conduit, used in areas that require bending around corners, movement, or vibration absorption.
Let’s take a closer look at how these materials behave in real-world conditions.
PVC electrical conduit, or polyvinyl chloride conduit pipe, is a type of thermoplastic known for being lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and electrically non-conductive.
In terms of physical performance, PVC conduit pipe typically offers a tensile strength around 5,000–8,000 psi, and is heat-rated up to 90°C (194°F) or much higher for continuous use.
These values can vary by manufacturer and specific product formulation, so it’s always a good idea to consult the supplier or product datasheet for exact specifications when making a purchase.
However, it may become brittle in cold weather and soften when exposed to high heat.
Steel conduit is much stronger and more impact-resistant. Made from galvanized or stainless steel.
Steel conduit offers tensile strength between 30,000 and 60,000 psi, excellent durability in high-traffic areas, and far better heat tolerance than PVC—often functioning in environments exceeding 400–500°C, depending on the application and protective coatings.
However, it’s heavier, conductive, and may corrode if not properly protected.
UL, IEC, AS/ NZS and CSA provide specific testing and classification methods, they all aim to ensure conduits meet core performance needs—mechanical strength, insulation, fire safety, and long-term reliability.
| Type | Standards |
|---|---|
| Rigid Conduit | UL 651 STANDARD FOR SAFETY Schedule 40, 80, Type EB and A Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings
IEC 61386-21 Conduit systems for cable management -Part 21: Particular requirements-Rigid conduit systems AS/NZS 2053.2 Conduits and fittings for electrical installations Part 2: Rigid plain conduits and fittings of insulating material AS/NZS 2053.3 Conduits and fittings for electrical installations Part 3: Rigid plain conduits andfittings of fibre-reinforced concrete material AS/NZS 2053.7 Conduits and fittings for electrical installations Part 7: Rigid metal conduits and fittings CSA C22.2 No. 45.1:22 Electrical rigid metal conduit-Steel CSA C22.2 No. 211.2-06 (R2021) Rigid PVC(unplasticized) conduit |
| Flexible Conduit | UL 1653 STANDARD FOR SAFETY Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing
IEC 61386-23 Conduit systems for cable management-Part 23: Particular requirements-Flexible conduit systems AS/NZS 2053.4 Conduits and fittings for electrical installations Part 4:Flexible plain conduits and fittings of insulating material AS/NZS 2053.8 Conduits and fittings for electrical installations Part 8:Flexible conduits and fittings of metal or composite material CSA C22.2 No. 227.1 Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing |
3. Installation and Handling of PVC Conduit and Steel Conduit
When it comes to installation, the differences between PVC and steel conduit become immediately obvious—especially to anyone who’s actually had to run several hundred feet of it on-site.
PVC conduit is often favored on job sites for one simple reason: it’s easy to work with. It’s light enough for one person to carry several sticks at once, and can be cut with a simple handsaw or even a fine-toothed blade. There’s no need for threading equipment or heavy-duty tools—just a clean cut and a deburring tool to smooth the edge.
Joining conduits and installing fittings for corner turns is also simple.
Most rigid PVC conduits use a solvent welding process: apply primer and cement, push the fittings together, and you’re done. It chemically bonds in a few minutes and sets quickly.
For flexible PVC, connectors usually snap or screw into place with a compression or locking ring—no heat, no glue.
Some types of PVC conduit can be bend with a heat gun or bending heater. With the right technique, it’s possible to make smooth bends around corners without special fittings.
In short: PVC is lightweight, requires minimal tooling, and installs fast.
Steel conduit installation is a different experience entirely. It’s heavier, tougher—and more demanding, both in terms of tools and physical labor.
There are usually three types of steel conduit: RMC, IMC, and EMT.
EMT is thinner and lighter, so in some classifications, it’s not considered a “true” rigid conduit.
Compared to PVC conduit, installing steel conduit like RMC or IMC is more labor-intensive. It typically requires cutting with a pipe cutter or hacksaw, threading the ends with manual or powered tools, and using thread sealant, bushings, or locknuts for secure connections.
If the metal-to-metal connection isn’t solid, a bonding jumper (a wire) is added to keep the system electrically continuous.
Bending steel conduit takes more effort—mechanical or hydraulic benders are often needed, and larger sizes may require powered equipment.
EMT, though lighter, still demands skill and force to bend with a hand bender.
Steel conduits do offer unmatched strength and protection, but from a labor standpoint, they take more time, more tools, and more training to install correctly.
4. Cost Analysis of PVC Conduit and Steel Electrical Conduit
When budgeting for an electrical conduit installation, material cost is one of the most visible expenses.
There are several other factors that can influence the total cost of a conduit system, including transportation, labor, installation accessories, and long-term maintenance.
💵 Material Price (Reference Only)
We searched a range of commercial sources to get a sense of typical market prices for both PVC and steel conduits.
| Conduit Type | Size | Approx. Price per Foot |
|---|---|---|
| PVC Schedule 40 | 1/2 inch | ~$0.51 |
| PVC Schedule 40 | 4 inch | ~$3.73 |
| Rigid Steel Conduit | 3/4 inch | ~$2.80 |
| Rigid Steel Conduit | 4 inch | ~$97.60 (bulk retail) |
💡 Note: Actual prices can vary depending on supplier, product quality, manufacturing process, and even region. They may fluctuate due to material costs, inventory levels, or supplier pricing models. Always confirm with the supplier at the time of purchase.
🚛 Transportation Costs
PVC conduits are significantly lighter in weight, which means lower shipping costs, especially for large-volume orders or remote site deliveries.
Steel conduits, being heavier and bulkier, typically cost more to transport and may require special handling.
🛠 Labor and Handling
Labor is another major cost driver. PVC conduits are easier to cut, join, and bend using basic hand tools. This speeds up installation and reduces labor hours—especially helpful on large-scale or fast-track projects.
Steel conduit is harder to work with compared to other types. It needs to be threaded, bent, and properly grounded. It may need specialized tools and more skilled workers to install it, so it typically takes longer to complete the job.
⏱ One case study showed that installing PVC can be up to 30–40% faster than steel in indoor commercial applications.
🔩 Accessories and Tools
Each conduit system comes with its own set of fittings and accessories. The cost of these accessories—both in money and time—should be factored into your total budget.
🧰 Long-Term Maintenance and Repair
PVC is resistant to rust and chemical corrosion, which reduces the need for protective coatings or replacements. However, it may degrade under UV exposure or extreme heat over time.
Therefore, we recommend using solar conduit for outdoor applications under direct sunlight.
If you are interested in solar conduit, you can read this post Everything You Need to Know About Solar Conduit.
And in the other hand, steel conduit pipe offers long-term strength, but may require anti-corrosion treatment, especially in humid or coastal environments, adding to upkeep costs.
5. Conclusion
Choosing between PVC and steel conduit depends on many factors — from material properties and installation ease to cost, environmental conditions, and safety requirements.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer to which conduit is better. By looking at all the factors—material, cost, installation, and environment—the best choice is always the one that fits your specific project needs.
PVC offers lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective solutions ideal for many applications, while steel provides superior strength and fire resistance where mechanical protection is critical.
At Ctube, we supply a wide range of PVC conduits, including both rigid conduit and flexible conduit types, all certified to meet industry standards such as UL, CSA, and others.
Whether your project demands durability, flexibility, or compliance, our products are designed to deliver reliable performance.
Thank you for reading! We wish your electrical projects great success.
If you’re interested in our conduits, feel free to contact us anytime.