Tabla de contenido
Palanca1. Introducción
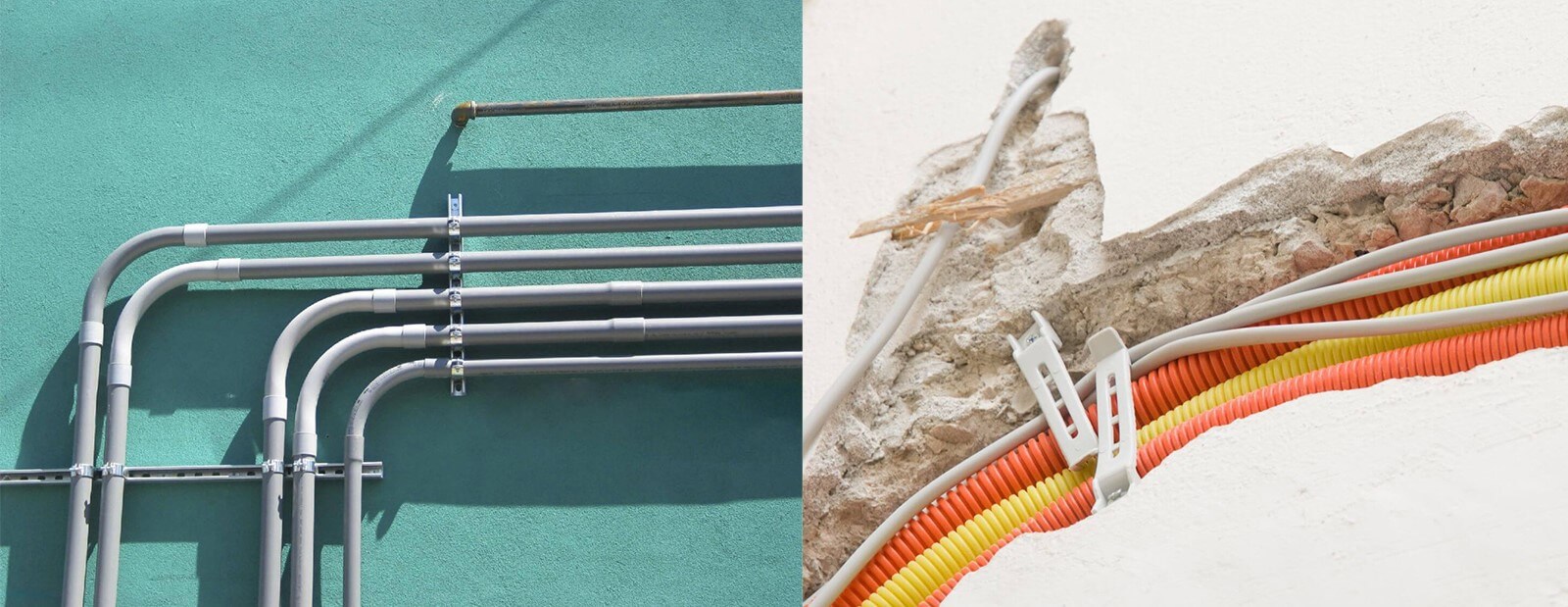
In electrical systems, conduit plays a vital role in protecting wires and ensuring reliable operation.
Rigid conduit comes in a variety of materials, including galvanized steel, aluminum, stainless steel, fiberglass, PVC-coated metal, and rigid PVC. Each type is designed to meet specific performance needs, such as corrosion resistance, strength, or non-metallic insulation.
Likewise, flexible conduit is available in several material options such as flexible metal conduit (FMC), liquid-tight flexible metal conduit, HDPE conduit, and flexible PVC conduit.
These options provide the versatility needed for installations in tight spaces, around corners, or where frequent movement is expected.
Among these options, rigid PVC conduit and flexible PVC conduit stand out as two of the most popular non-metallic choices, widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial projects.
Though they share a common material—polyvinyl chloride—their physical structure, performance characteristics, and installation methods differ significantly.
In this post, we’ll explore the key differences between these two types of PVC conduits.
Whether you’re an electrical engineer, project contractor, or procurement professional, gaining a clear understanding of rigid and flexible PVC conduits will help you make smarter, more efficient decisions for your electrical installations.
2. What is Rigid PVC Conduit?
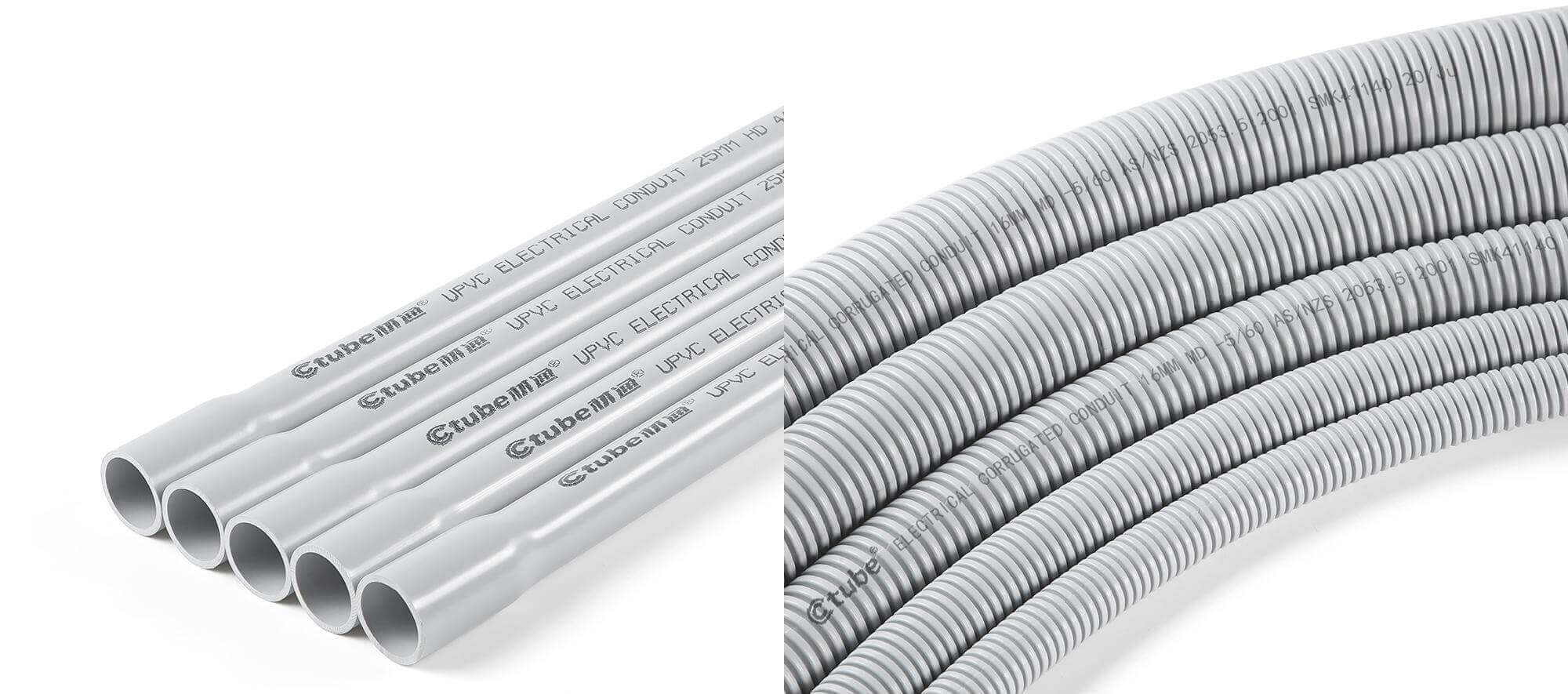
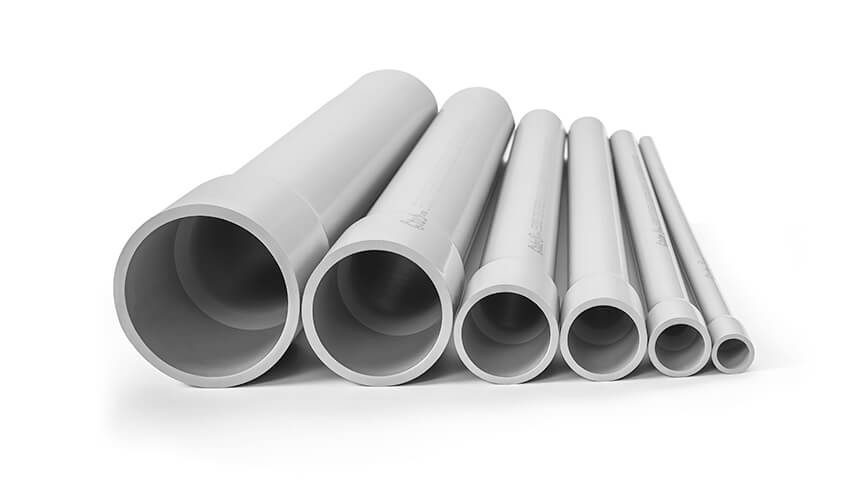
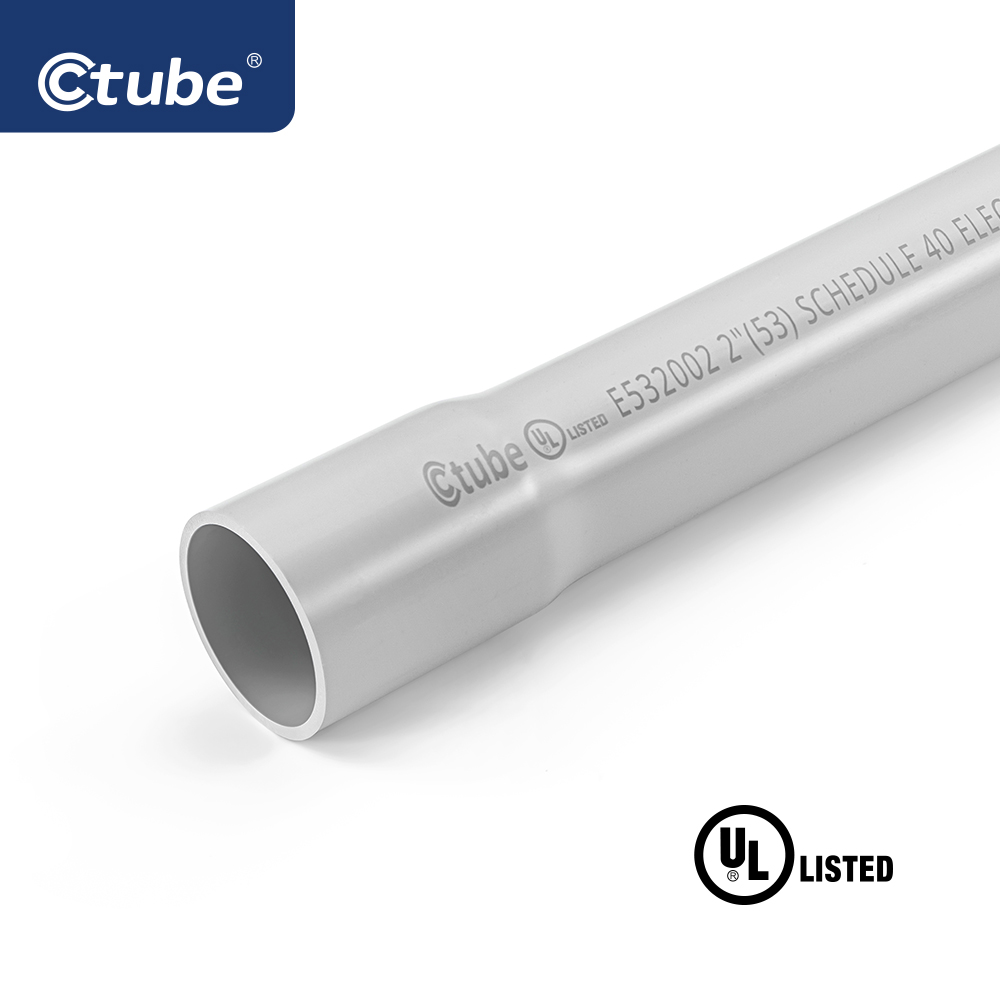
Rigid PVC conduit is a non-metallic conduit known for its straight, sturdy structure and smooth inner surface. It serves as a durable, non-conductive alternative to metal conduit systems such as RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit) or EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing).
PVC rigid conduit is manufactured from polyvinyl chloride, which offers excellent rigidity, chemical resistance, and long-term durability. This kind of rigid conduit is typically used to protect and route electrical wiring in commercial, industrial, and underground applications.
Rigid PVC conduit pipe is usually sold in 10-foot (3-meter) or 20-foot (6-meter) lengths, with or without integrated bells for easier joining. The rigid form allows for long, straight runs with minimal sagging or deformation.
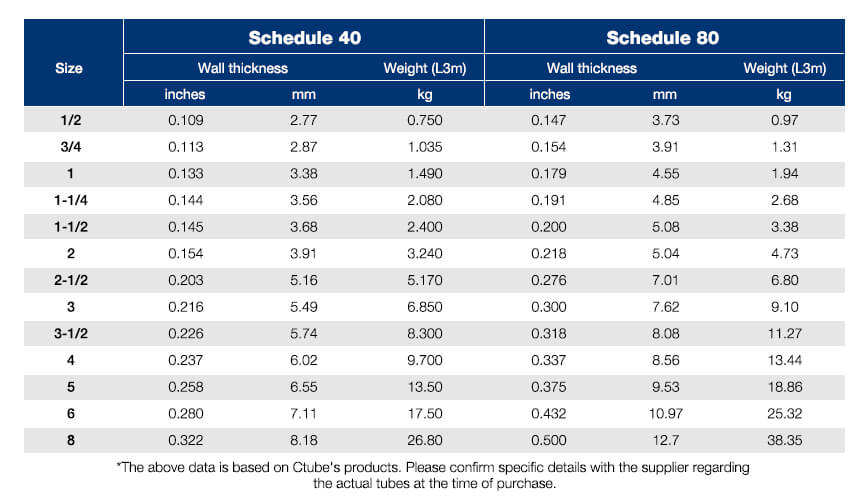
Two of the most common classifications are Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduits, both defined by wall thickness and pressure ratings.
Schedule 40 conduits have thinner walls and are easier to cut and install.
Schedule 80 conduits feature thicker walls and are used in industrial or heavy-duty environments where additional mechanical protection is needed.
For example, a 1-inch Ctube Conducto Schedule 40 typically has a wall thickness of 0.133 inches, while the same size in Anexo 80 has a wall thickness of 0.179 inches, providing increased impact resistance.
Electrical rigid PVC conduits are commonly available in sizes ranging from ½ inch to 6 inches (or 16 mm to 155 mm, depending on regional standards). Some even offer 8 inches for large projects.
The rigidity ensures stable support for long cable runs, with the conduit often secured using clamps or conduit straps. Compared to ENT (flexible PVC conduit we wll introduce in the following), it requires pre-measured bends using heat or pre-formed elbows.
3. What is Flexible PVC Conduit (ENT)?
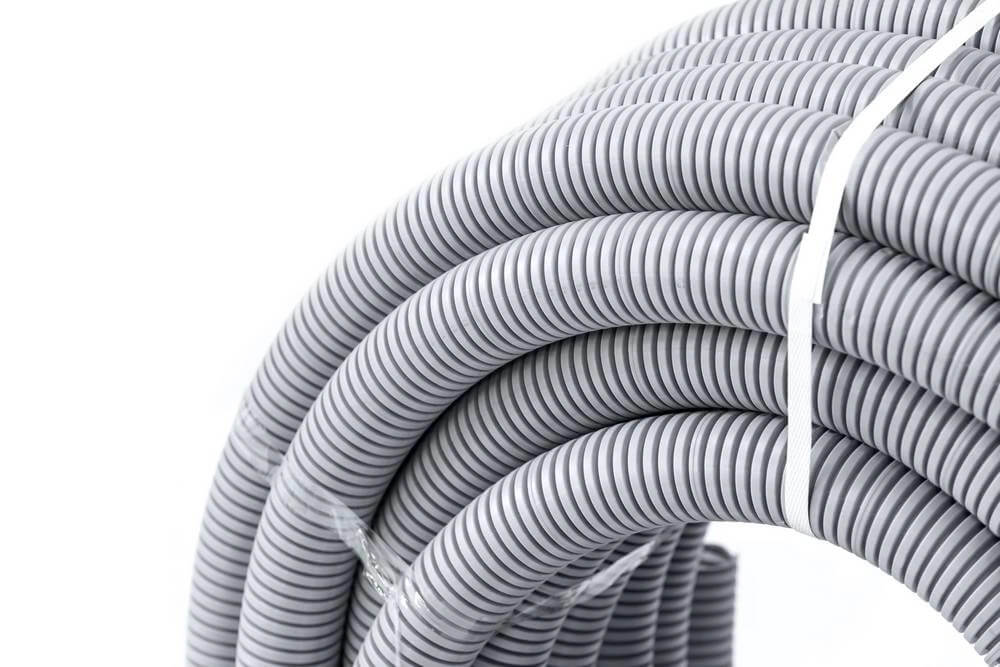
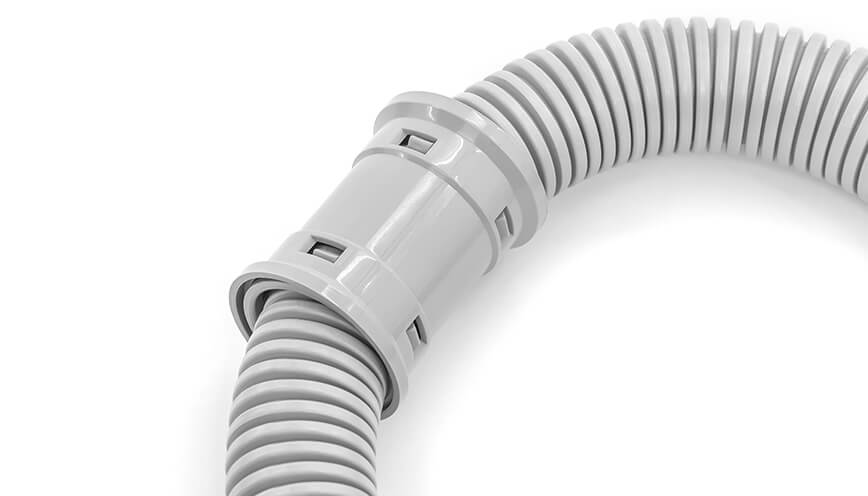
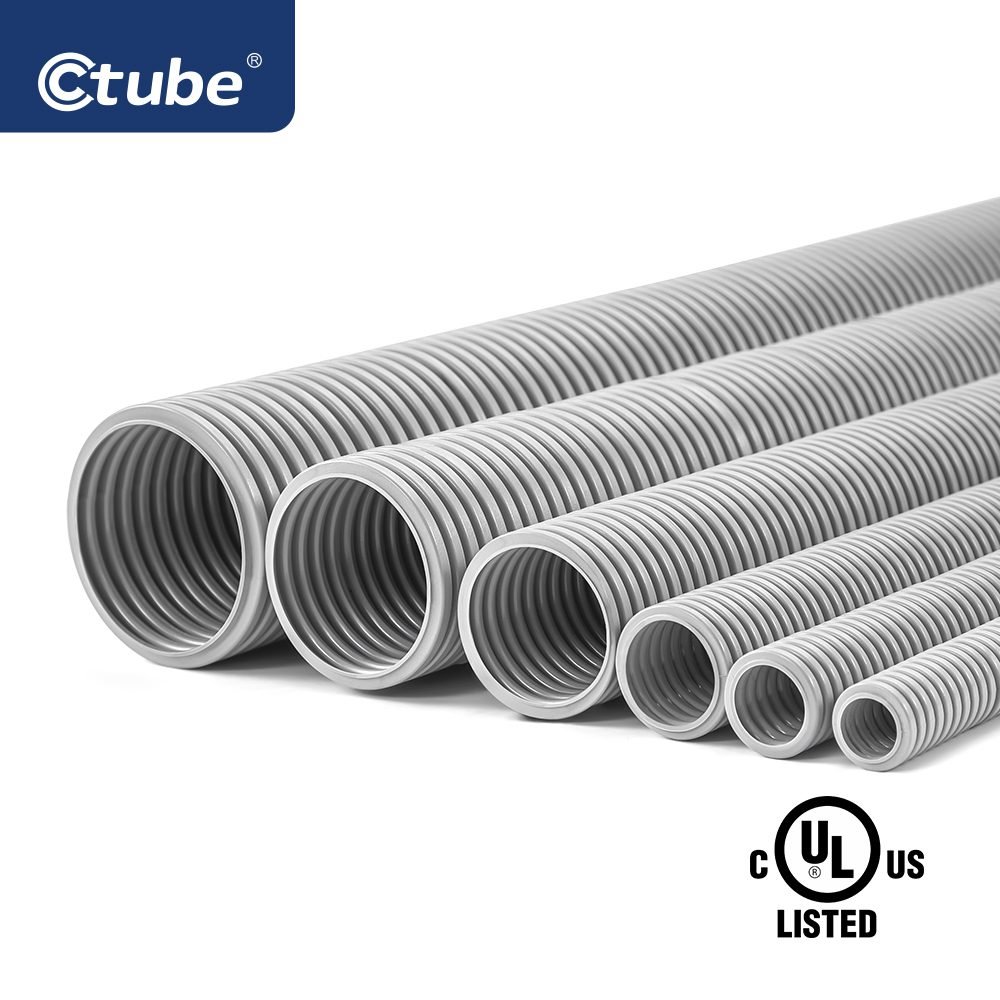
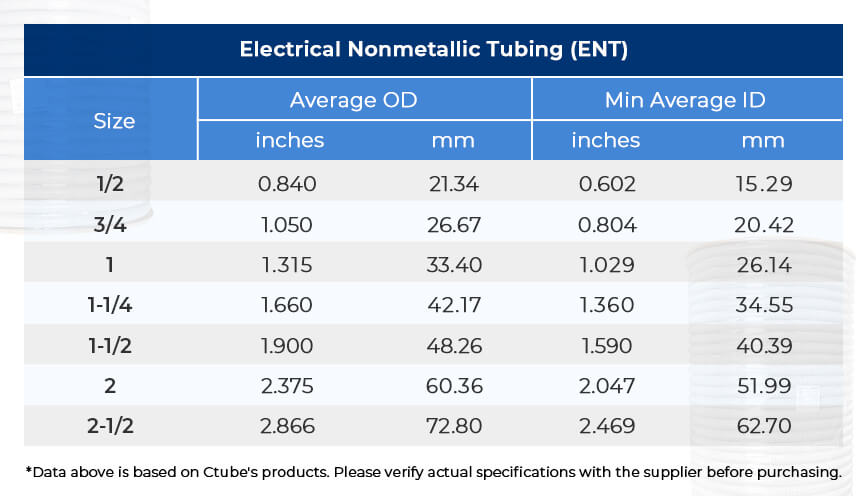
Flexible PVC conduit, often referred to as PVC Corrugated Conduit or Tubos eléctricos no metálicos (ENT), is a type of nonmetallic conduit designed for applications requiring greater routing flexibility.
Flexible PVC conduits, especially corrugated ones, usually have a wavy or ridged shape on both the inside and outside. These raised ridges are called corrugations, and they help the conduit bend easily without breaking. Even though the surface has this ridged pattern, it still feels smooth to the touch, not rough or sharp.
Unlike rigid conduits, ENT can be bent by hand, making it especially suitable for installations in walls, ceilings, or other confined spaces where rigid systems are impractical.
ENT is commonly available in nominal sizes ranging from ½ inch to 2½ inches (or approximately 16 mm to 63 mm in metric), similar to rigid PVC conduit.
The wall thickness of ENT is thinner than SCH 40 or SCH 80, allowing for flexibility, and most ENT conduits are provided in coil form, typically 25 to 100 feet ( approximately 7.6 to 30 meters) per roll, depending on diameter. This coiled packaging enhances ease of transport and installation in long, curved runs. At Ctube, we support customized packaging based on project-specific needs.
PVC flexible conduit also made from polyvinyl chloride as we mentioned about, the different molds, machines, and added ingredients make one type rigid and the other flexible.
4. Comparison Between Rigid PVC Conduit and Flexible PVC Conduit
Now that we’ve learned the basics about rigid PVC conduit and flexible PVC conduit, let’s compare them side by side.
4.1 What Rigid and Corrugated PVC Electrical Conduits Have in Common
Before diving into their differences, it’s helpful to know that rigid and corrugated PVC conduits also share several things in common.
First, both are made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) as their base material. This gives them similar advantages such as corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and light weight compared to metal conduits. They are also both non-conductive and safe for electrical applications.
They are flame-retardant when formulated correctly, and can be made UV-resistant for outdoor use.
Second, they typically follow the same color-coding standards. For example, gray is commonly used for electrical systems, while orange is often used for telecommunications. This helps ensure consistency on job sites and supports compliance with industry regulations.
While they have these similarities, the key differences in structure, flexibility, strength, and installation methods make each type better suited for different kinds of projects. Let’s explore those differences next.
4.2 Rigid and Corrugated PVC Conduits: Differ in Production, Materials & Shapes
PVC Rigid conduit is produced through a standard extrusion process.
The PVC is melted and pushed through a mold to form a smooth, straight pipe.
PVC Corrugated conduit, on the other hand, as the PVC is pushed out, it goes through a fast-moving mold that forms the wave-like ridges.
The materials used in each type are also different. These differences in ingredients are what give each conduit its unique properties—rigid for strength, corrugated for flexibility.
Rigid PVC conduit uses a harder type of PVC with fillers like impact modifiers and stabilizers. This makes it strong, durable, and suitable for heavy-duty use.
PVC corrugated conduit sometimes add more plasticizers than PVC rigid conduit to make the material soft and flexible.
4.3 Installation Methods and Fittings Differences between Rigid and Corrugated PVC Conduits
One of the key factors that differentiates these two types of conduits is how they are installed and the types of fittings they require.
One major difference between rigid and flexible PVC conduit is the use of solvent cement, often called glue.
Rigid PVC conduit usually requires solvent cement to create strong, permanent joints. When installing, the ends of the conduit and fittings are coated with this special glue, which chemically softens the plastic surfaces so they bond tightly together. Once cured, the connection is waterproof and durable—ideal for long-term or outdoor installations.
In contrast, flexible PVC conduit does not typically use solvent cement. Because of its flexible and ribbed design, it connects with snap-in or threaded fittings instead.
Another distinguish different is the usage of conduit fittings and accessories.
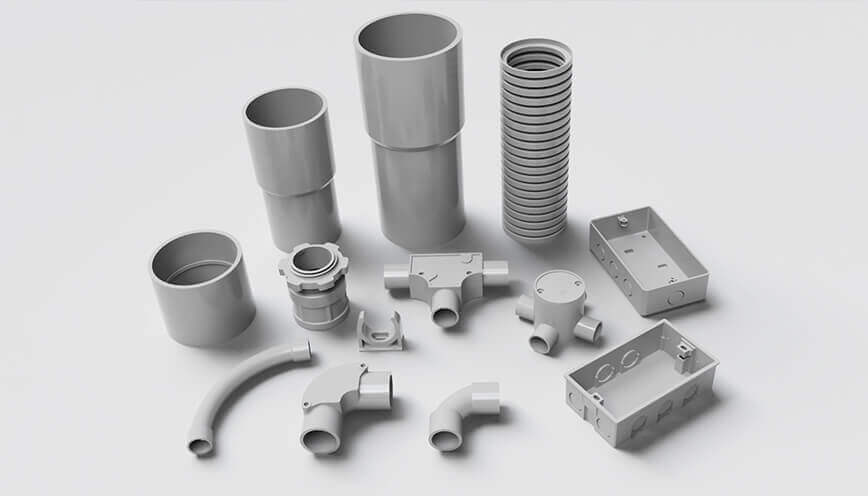
Fittings are essential components used to connect, support, or change the direction of conduit systems.
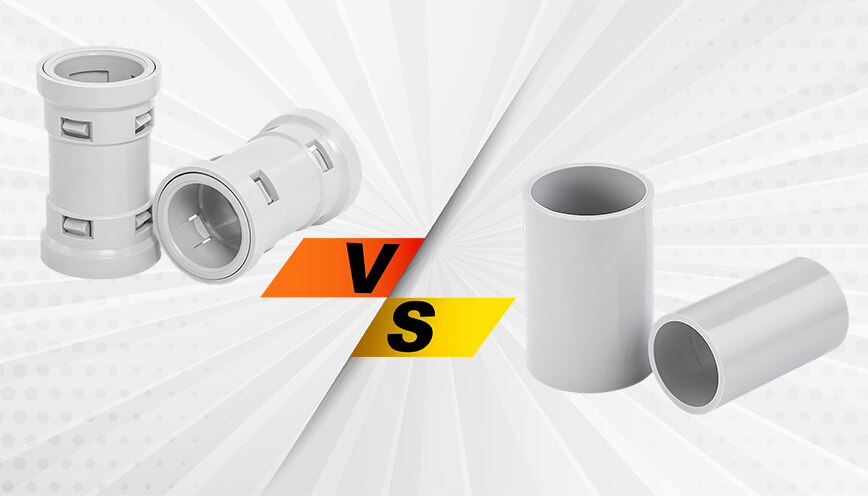
Both rigid PVC conduit and flexible (corrugated) PVC conduit use fittings, and many of their basic functions are similar.
For example, couplings are used to join two conduit sections, and male adapters help connect the conduit to electrical boxes or equipment.
However, because the two types of conduits are shaped and designed differently, their fittings are not exactly the same.
Rigid conduit cannot bend on its own, so it needs more types of fittings to help change direction. Common fittings include elbows, sweep bends, and T-junctions, which allow the conduit to turn corners or split into different paths.
On the other hand, flexible conduit can bend and curve naturally, so it needs fewer fittings. Most of the time, simple connectors, end caps, or male adapters are enough. Because it can move easily, there’s usually no need for special parts to help it turn.
4.4 Mechanical Durability of Rigid and Flexible PVC Conduit
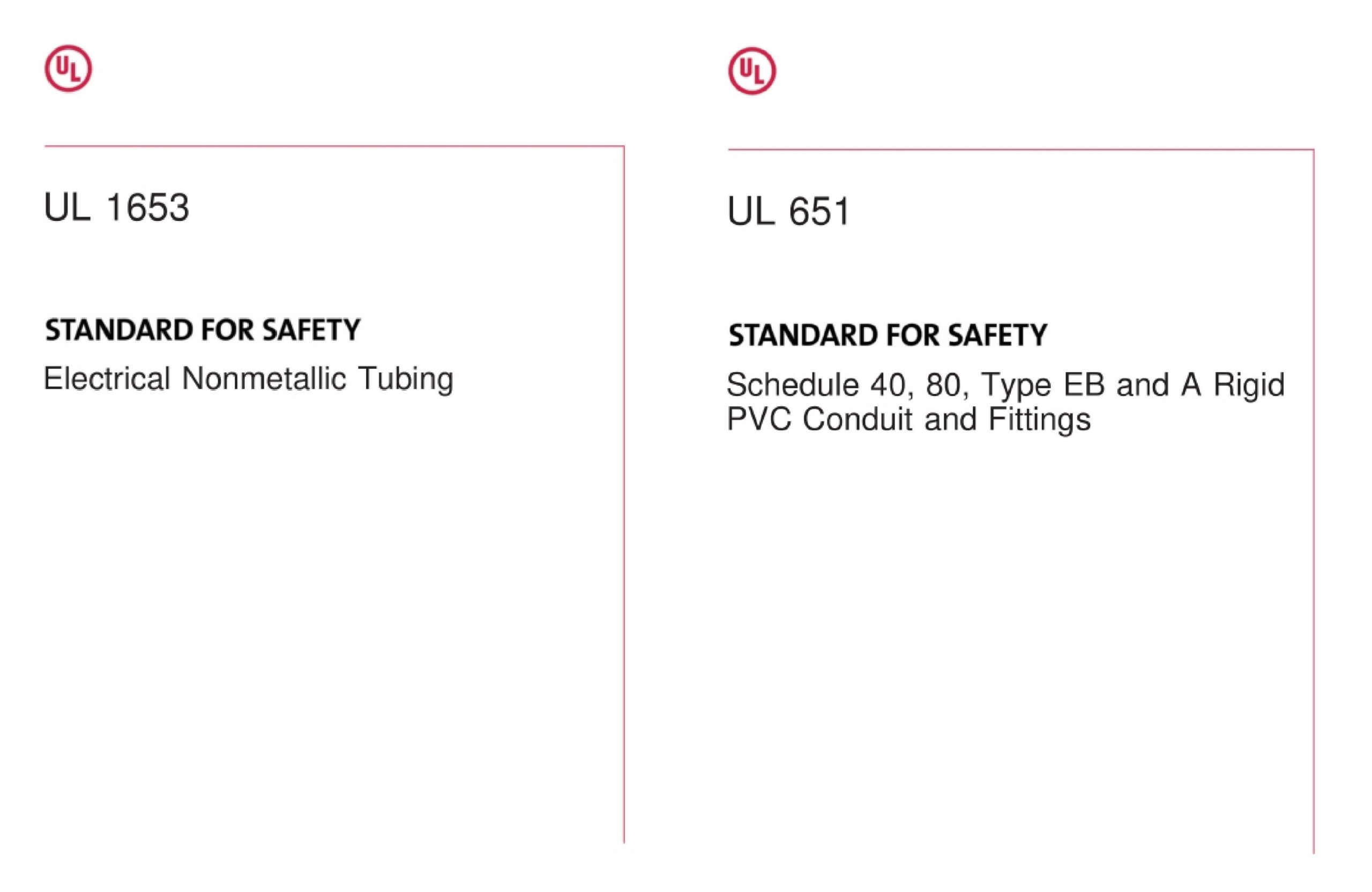
When it comes to mechanical strength, rigid and flexible PVC conduits are tested under different standards. Here we use UL standards as the examples, UL 651 for rigid PVC conduit and UL 1653 for ENT conduit.
These standards reflect the different mechanical demands placed on each product in real-world use.
Rigid PVC conduit, tested under UL 651, must pass crush tests, impact tests, and tensile strength evaluations.
It’s designed to handle high mechanical stress, such as being buried underground or installed in exposed outdoor areas where it might be stepped on, driven over, or subjected to other physical impacts.
These tests confirm that rigid conduit can maintain shape and protection even under pressure.
In contrast, electrical nonmetallic tubing, which follows UL 1653, is tested with lower mechanical load requirements.
Since it is used mostly in interior or low-impact environments, the standard focuses more on flexibility, pull strength, and bending performance rather than heavy-load resistance.
Flexible conduit is built to adapt to curves and tight spaces, not to bear weight.
In summary, rigid PVC conduit offers superior mechanical strength and is better suited for heavy-duty or outdoor environments. Flexible conduit offers ease of routing and adaptability, but should be used in areas with minimal physical stress.
That’s why many projects choose PVC rigid conduit for underground installations, either for direct burial or encasement in concrete, while ENT (flexible PVC conduit) is often not recommended to used underground or even prohibited for direct burial in certain locations due to its lower mechanical strength.
5. Choosing Between PVC Rigid Conduit and Flexible Conduit
Now that we’ve introduced the basic characteristics of PVC rigid conduit and flexible conduit, and compared their key differences, you may already have a clearer picture of the each one.
To help you make the right decision for your project, let’s now take a closer look at the main factors you should consider when choosing between the two.
Video for you to learn more.
5.1 Consider the Installation Environment
Rigid PVC conduit is ideal for underground installations, outdoor use, or high-impact areas. Its strong structure allows for direct burial, concrete encasement, and exposure to physical pressure.
Flexible PVC conduit is more suitable for indoor installations, tight spaces, or areas requiring frequent changes in direction. For example, it’s ideal for wiring that needs to pass through walls, run above ceilings, or navigate around tight corners without requiring many fittings.
5.2 Evaluate Mechanical Strength Requirements
If your project involves heavy mechanical loads, such as areas where conduits may be stepped on or buried, rigid conduit is the safer choice.
Flexible conduit cannot withstand the same amount of pressure and should be avoided in situations where crushing or impact is likely.
5.3 Check Compliance with Local Codes
It’s important to always follow local regulations when choosing and installing conduit.
Different countries and regions have their own rules about which types of conduit can be used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications, including for underground installations. These regulations ensure safety and proper functionality.
Before making your final decision, be sure to consult your local electrical code or speak with an engineer to ensure compliance with the applicable standards.
5.4 Cost and Budget Considerations
When choosing between PVC rigid conduit and flexible conduit, cost is a significant factor.
Rigid conduit tends to be more expensive due to its higher material strength and the need for additional fittings such as elbows and couplings. However, its durability and suitability for harsh conditions may make it a more cost-effective long-term solution.
On the other hand, flexible conduit is generally less expensive, especially for smaller projects or installations that require quick and easy routing.
While it may have a lower upfront cost, it might not suitable for areas exposed to physical stress or harsh environments.
6. Conclusión
Both PVC rigid conduit and flexible PVC conduit offer unique advantages depending on the needs of your project.
Rigid conduit provides strength, protection, and durability, on the other hand, flexible conduit is easier to install, more versatile.
When selecting the right conduit, it’s important to consider factors such as the installation environment, compliance with local codes, cost, and long-term performance.
En Tubo C, we are committed to providing high-quality PVC rigid conduit, flexible conduits and matching conduit fittings and accessories such as junction boxes, adaptable boxes, elbows, sweep bends, couplings, and more.
They meet international standards such as UL, CSA, y Norma AS/NZS 2053. Also provide special series solar UPVC conduits, LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits.
Our products meet the demands of various installations, whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial applications.
🎯 Want to learn more about electrical conduit, installation tips, and the latest industry updates?
📩 Follow Ctube on LinkedIn or other social media like Facebook or Instagram or YouTube, we regularly share helpful information about PVC conduit, fittings, and best practices for electrical projects — whether you’re a contractor, engineer, or just planning your next project.
📚 Read more helpful post from our blog pages to learn more about conducto eléctrico.
Thank you for reading. We hope this article has been helpful in guiding your conduit selection. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to contact us. We wish you great success with your project!