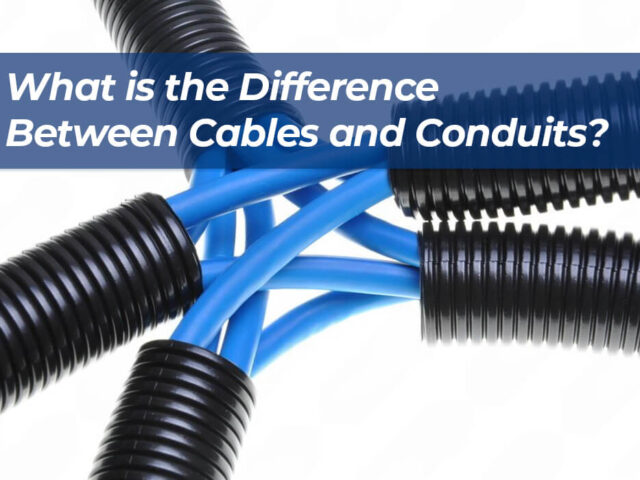
1. Introdução Ao trabalhar em um projeto elétrico, é comum ver cabos e conduítes comprados juntos. Na verdade, muitos...
Leia mais
Blogue
Como dobrar conduítes elétricos sem um dobrador
Ctubeoficialchina – 22 de julho de 2025
1. Introdução “Posso dobrar um conduíte elétrico sem uma ferramenta especial?” Essa é uma pergunta comum entre pessoas que trabalham com instalações elétricas...
Leia mais
O que você precisa saber antes de instalar conduítes aparentes
Ctubeoficialchina – 5 de julho de 2025
1. Introdução Quando pensamos em eletrodutos, muitas vezes os imaginamos escondidos atrás de paredes ou tetos. Mas em muitos...
Leia mais
Um guia completo para curvas e cotovelos de PVC em sistemas de eletrodutos
Ctubeoficialchina – 5 de julho de 2025
1. Introdução Em qualquer sistema de eletrodutos, os trechos retos de tubulação são apenas o começo. Para contornar curvas, evite obstáculos estruturais...
Leia mais
PVC vs. Metal vs. RTRC vs. LSZH vs. HDPE, o guia definitivo para materiais de conduítes elétricos (2025)
Ctubeoficialchina – 2 de abril de 2025
1. Introdução Um tubo de conduíte elétrico é um sistema de tubulação de proteção projetado para abrigar e proteger a fiação elétrica de danos mecânicos...
Leia mais
Guia definitivo para canalização de cabos: tipos de projeto, tamanhos, regulamentações e práticas recomendadas
Ctubeoficialchina – 31 de março de 2025
1. Introdução aos sistemas de canaletas de cabos As canaletas de cabos são um componente essencial das instalações elétricas, projetadas para abrigar e proteger...
Leia mais
Conduíte de PVC padrão IEC 61386 – Tudo o que você precisa saber
Ctubeoficialchina – 24 de março de 2025
1. Introdução Quando se trata de instalações elétricas, selecionar o conduíte certo é crucial para garantir segurança, durabilidade e desempenho....
Leia mais
Os 10 principais fabricantes e fornecedores de tubos PPR na China
Ctubeoficialchina – 1 de março de 2025
1. 联塑 (LESSO Group) Introdução: Fundado em 1986 e listado na Bolsa de Valores de Hong Kong (HKEX: 2128), o LESSO Group...
Leia mais
Os 10 maiores fabricantes e fornecedores de tubos PPR do mundo
Ctubeoficialchina – 1 de março de 2025
Tubos de PPR (copolímero aleatório de polipropileno) se tornaram um pilar fundamental na infraestrutura moderna devido à sua durabilidade, resistência à corrosão e...
Leia mais
Guia para selecionar o melhor conduíte para seu projeto de fibra óptica
Ctubeoficialchina – 1 de fevereiro de 2025
1. Introdução 1.1 Visão geral das instalações de fibra óptica A tecnologia de fibra óptica é a espinha dorsal da comunicação moderna, permitindo internet de alta velocidade,...
Leia mais
Opções infinitas para suas necessidades específicas
A Ctube se concentra no setor de conduítes elétricos de plástico, atendendo à demanda do cliente por produtos, tecnologia e serviços.
Sempre tomamos medidas adicionais para deixar nossos clientes satisfeitos com a qualidade, eficiência e comercialização de nossos produtos. Com alta qualidade e uma ampla gama de produtos, estabelecemos uma cooperação de longo prazo com muitos clientes de diferentes áreas do mundo.
Solicite um orçamento
Pronto para trabalhar junto? Construa um projeto conosco!