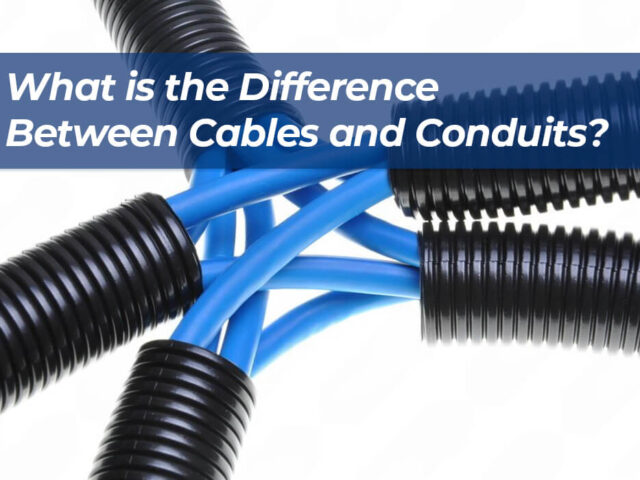
1. Introducción Al trabajar en un proyecto eléctrico, es común ver que los cables y conductos se compran juntos. De hecho, muchos...
Lee Mas
Blog
Cómo doblar conductos eléctricos sin dobladora
Ctube oficial de China – 22 de julio de 2025
1. Introducción "¿Puedo doblar conductos eléctricos sin una herramienta especial?" Es una pregunta frecuente entre quienes trabajan con electricidad...
Lee Mas
Qué debe saber antes de instalar un conducto expuesto
Ctube oficial de China – 5 de julio de 2025
1. Introducción. Cuando pensamos en conductos eléctricos, solemos imaginarlos ocultos tras paredes o techos. Pero en muchos...
Lee Mas
Guía completa sobre codos y curvas de PVC en sistemas de conductos eléctricos
Ctube oficial de China – 5 de julio de 2025
1. Introducción. En cualquier sistema de conductos eléctricos, los tramos rectos de tubería son solo el comienzo. Para sortear las esquinas, evite...
Lee Mas
PVC vs. Metal vs. RTRC vs. LSZH vs. HDPE: La guía definitiva de materiales para conductos eléctricos (2025)
Ctube oficial de China – 2 de abril de 2025
1. Introducción Un conducto eléctrico es un sistema de tubería protectora diseñado para albergar y proteger el cableado eléctrico de daños mecánicos.
Lee Mas
Guía definitiva sobre canalizaciones para cables: tipos de diseño, tamaños, normativas y prácticas recomendadas
Ctube oficial de China – 31 de marzo de 2025
1. Introducción a los sistemas de canalización de cables La canalización de cables es un componente esencial de las instalaciones eléctricas, diseñado para alojar y proteger...
Lee Mas
Conducto de PVC según la norma IEC 61386: todo lo que necesita saber
Ctube oficial de China – 24 de marzo de 2025
1. Introducción Cuando se trata de instalaciones eléctricas, seleccionar el conducto adecuado es crucial para garantizar la seguridad, la durabilidad y el rendimiento.
Lee Mas
Los 10 principales fabricantes y proveedores de tuberías PPR en China
Ctube oficial de China – 1 de marzo de 2025
1. 联塑 (LESSO Group) Introducción: Fundado en 1986 y cotizado en la Bolsa de Valores de Hong Kong (HKEX: 2128), LESSO Group...
Lee Mas
Los 10 principales fabricantes y proveedores de tuberías PPR del mundo
Ctube oficial de China – 1 de marzo de 2025
Las tuberías de PPR (copolímero aleatorio de polipropileno) se han convertido en una piedra angular en la infraestructura moderna debido a su durabilidad, resistencia a la corrosión y...
Lee Mas
Guía para seleccionar el mejor conducto para su proyecto de fibra óptica
Ctube oficial de China – 1 de febrero de 2025
1. Introducción 1.1 Descripción general de las instalaciones de fibra óptica La tecnología de fibra óptica es la columna vertebral de las comunicaciones modernas, permitiendo Internet de alta velocidad,...
Lee Mas
Opciones infinitas para sus necesidades específicas
Ctube se centra en el campo de los conductos eléctricos de plástico, en torno a la demanda de productos, tecnología y servicios del cliente.
Siempre tomamos medidas adicionales para que nuestros clientes estén satisfechos con la calidad, eficiencia y comercialización de nuestros productos. Con alta calidad y una amplia gama de productos, hemos establecido una cooperación a largo plazo con muchos clientes de diferentes áreas del mundo.
Solicitar cotización
¿Listo para trabajar juntos? ¡Construye un proyecto con nosotros!