Tabla de contenido
PalancaEn las industrias dominadas por productos eléctricos, como la industria de conductos eléctricos, es absolutamente esencial cumplir con estándares de fabricación estrictos. Garantizar que estos productos se sometan a pruebas rigurosas y certifiquen su calidad es igualmente fundamental. Esto no solo garantiza que los productos estén libres de defectos, sino que también minimiza el riesgo de fallas que podrían provocar problemas graves para los usuarios. Sin estándares y certificaciones establecidos, el mercado se inundaría de productos eléctricos de calidad inferior, lo que aumentaría la probabilidad de fallas frecuentes, daños e incluso lesiones.
Como fabricante líder de conductos eléctricos, reconocemos el papel fundamental que desempeña la certificación de productos para mantener la seguridad, la calidad y el cumplimiento de las normas de la industria. Al buscar un fabricante de conductos o conductos eléctricos calificado, es fundamental comprender las marcas de certificación, los laboratorios de pruebas y los términos relacionados. A continuación, se incluye una guía que lo ayudará a comprender estos aspectos:
1. Acerca de las SDO y los organismos de certificación
Las Organizaciones de Desarrollo de Normas (SDO, por sus siglas en inglés) y los Organismos de Certificación son componentes esenciales del ecosistema regulatorio y de garantía de calidad, y cada uno de ellos desempeña un papel distinto pero complementario. Las SDO son las principales responsables de crear y mantener normas que describen los requisitos, las directrices y las características específicas que deben cumplir los productos, los servicios y los sistemas. Estas normas garantizan la coherencia, la seguridad y la calidad en todas las industrias y se desarrollan a través de un proceso de consenso en el que participan diversas partes interesadas, incluidos expertos de la industria, agencias gubernamentales y representantes de los consumidores.
Las organizaciones de normalización, como el Instituto Nacional Estadounidense de Normas (ANSI), la Organización Internacional de Normalización (ISO) y ASTM International, se centran en establecer las normas y directrices que deben seguir las industrias. Estas normas suelen ser voluntarias, a menos que las adopten los organismos reguladores, pero sirven como base para garantizar que los productos y servicios sean fiables y seguros. El principal resultado de las organizaciones de normalización es la publicación de estas normas, que proporcionan un marco para que los fabricantes y los proveedores de servicios garanticen la calidad y la interoperabilidad.
Por otro lado, los organismos de certificación desempeñan el papel crucial de garantizar que los productos, sistemas o servicios cumplan con los estándares establecidos por las organizaciones de normalización. Son organizaciones independientes autorizadas para realizar pruebas, inspecciones y auditorías. Los organismos de certificación como UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CSA (Canadian Standards Association) y ETL (Intertek) evalúan los productos para verificar que cumplen con los estándares y regulaciones pertinentes. Después de realizar pruebas rigurosas, emiten certificaciones que confirman el cumplimiento de un producto, a menudo indicado por una marca de certificación como la marca UL o la marca CSA.
Los organismos de certificación hacen más que simplemente probar productos; brindan una capa esencial de garantía a los consumidores, fabricantes y agencias regulatorias. Sus marcas de certificación son símbolos ampliamente reconocidos de calidad y seguridad, que ofrecen a los consumidores la confianza de que los productos que compran cumplen con estándares rigurosos. Para los fabricantes, la certificación es un paso crucial en el desarrollo de productos y la entrada al mercado, ya que garantiza el cumplimiento de los requisitos legales y mejora la comercialización.
En resumen, mientras que las SDO establecen las pautas y los estándares que deben seguir las industrias, los organismos de certificación validan el cumplimiento de estos estándares mediante pruebas y certificaciones. Ambas entidades son vitales para mantener la seguridad y la calidad de los productos y la confianza de los consumidores. Juntas, crean un sistema en el que los estándares no solo se definen sino que también se aplican de manera efectiva, lo que garantiza que los productos en el mercado sean seguros, confiables y de alta calidad.
2. ¿Qué es la certificación UL?
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) es una organización líder mundial en certificación de seguridad que garantiza la seguridad de los productos desde su creación en 1894. La misión principal de UL es crear un mundo más seguro mediante el desarrollo de estándares de seguridad rigurosos y la realización de pruebas integrales en una variedad de productos, incluidos componentes eléctricos, electrodomésticos, maquinaria industrial y más.
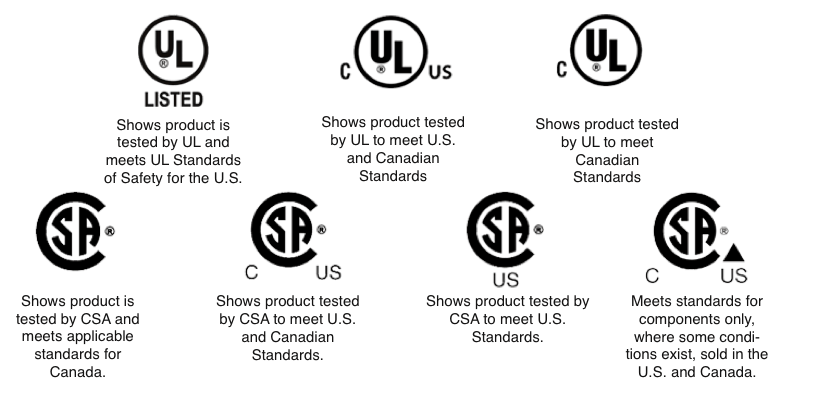
Marca UL: La marca UL es un símbolo de confianza y seguridad que indica que un producto ha sido sometido a pruebas rigurosas y cumple con los estándares de seguridad de UL. Esta marca se reconoce principalmente en los EE. UU. y es fundamental para los productos que se comercializan en esta región. La presencia de la marca UL en un producto significa que se lo ha evaluado para detectar posibles riesgos, como descargas eléctricas, peligros de incendio y peligros mecánicos, lo que garantiza que es seguro para el uso del consumidor.
Impacto global: Si bien la certificación UL es un requisito para muchos productos en los EE. UU., su influencia se extiende mucho más allá del mercado estadounidense. Muchos países e industrias reconocen a UL como un punto de referencia para la seguridad de los productos. Este reconocimiento global permite a los fabricantes con productos certificados por UL acceder a los mercados internacionales con mayor facilidad, ya que la marca UL a menudo cumple o supera los requisitos de seguridad de otras regiones.
Proceso de prueba: El proceso de pruebas de UL es exhaustivo y comprende varias etapas, incluida la evaluación del diseño del producto, los materiales y el rendimiento en diversas condiciones. Los productos se someten a pruebas de estrés para garantizar que puedan soportar el uso diario y posibles emergencias. En el caso de los productos eléctricos, UL realiza pruebas para detectar problemas como cortocircuitos, sobrecargas y resistencia a factores ambientales como la humedad y el calor. UL también realiza inspecciones periódicas de las instalaciones de fabricación para garantizar el cumplimiento continuo de sus normas.
3. ¿Qué es la certificación cUL?
La marca cUL es el equivalente canadiense de la certificación UL, que indica que un producto cumple con los estándares de seguridad exigidos por el Código Eléctrico Canadiense (CAN/CSA 22.1-12). Los productos con la marca cUL han sido probados y certificados para su uso seguro en Canadá, de acuerdo con los requisitos regulatorios específicos del país.
Consideraciones específicas del mercado: Los fabricantes que deseen vender sus productos tanto en los EE. UU. como en Canadá deben obtener las certificaciones UL y cUL para garantizar el cumplimiento de las normas de seguridad de cada país. Este proceso de doble certificación garantiza que los productos cumplan con los criterios de seguridad necesarios para ingresar a ambos mercados. Sin la certificación adecuada, los productos pueden enfrentar obstáculos regulatorios, lo que genera demoras en la entrada al mercado o posibles retiros de productos del mercado.
Etiquetado: Los productos certificados para ambos mercados suelen llevar marcas duales UL y cUL, que indican claramente su cumplimiento con las normas de seguridad tanto de los EE. UU. como de Canadá. Este etiquetado dual ayuda a los consumidores, minoristas y reguladores a identificar rápidamente los productos que son seguros y están aprobados para su uso en ambos países, lo que simplifica los procesos de compra y aprobación regulatoria.
4. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre UL y cUL?
Aunque tanto las certificaciones UL como las cUL son emitidas por Underwriters Laboratories, cada una de ellas se aplica a mercados diferentes. La certificación UL se aplica a productos destinados al mercado estadounidense, mientras que la certificación cUL se aplica a productos destinados al mercado canadiense. Cada certificación cumple con los estándares específicos de seguridad y rendimiento pertinentes para el país respectivo, en particular en lo que respecta a los requisitos de prueba, las consideraciones específicas del mercado y las prácticas de etiquetado y marcado.
Normas nacionales: La certificación UL se rige por las normas establecidas por los organismos reguladores de los EE. UU., mientras que la certificación cUL sigue las normas canadienses. Aunque estas normas están estrechamente relacionadas, reflejan los criterios de seguridad y rendimiento exclusivos de cada país. Por ejemplo, ciertos materiales o aspectos de diseño que son aceptables según las normas de los EE. UU. pueden requerir pruebas o modificaciones adicionales para cumplir con las normas canadienses. Las normas de voltaje eléctrico, las prácticas de cableado y otras normas de seguridad pueden diferir entre los EE. UU. y Canadá.
Procedimientos de prueba: Los procedimientos de prueba para las certificaciones UL y cUL pueden variar levemente debido a los diferentes entornos regulatorios. Las normas canadienses a menudo incorporan elementos influenciados por las normas europeas, lo que da lugar a pruebas adicionales o criterios diferentes para ciertos tipos de equipos. Esto puede incluir requisitos específicos de aislamiento eléctrico, resistencia al fuego o resiliencia ambiental que difieren de los utilizados en los EE. UU.
Cumplimiento normativo: Los productos destinados a la venta en Estados Unidos deben cumplir con las normas UL, mientras que los comercializados en Canadá deben cumplir con los requisitos de la cUL. Esta distinción es crucial para los fabricantes que aspiran a entrar en ambos mercados, ya que la obtención de ambas certificaciones puede agilizar las ventas transfronterizas y garantizar una aceptación más amplia en el mercado.
Expectativas del consumidor: En ambos países, los consumidores y los organismos reguladores suelen esperar que los productos lleven la marca de certificación correspondiente. En Canadá, la presencia de una marca cUL puede infundir mayor confianza en la seguridad del producto y en el cumplimiento de las normas locales, tal como lo hace la marca UL en los EE. UU.
Penetración del mercado: Los productos certificados con una sola marca pueden enfrentar desafíos para ingresar al otro mercado.
Doble marcado: Algunos productos pueden llevar tanto la marca UL como la marca cUL si han sido certificados para ambos mercados. Esta doble marca indica que el producto cumple con las normas de seguridad de ambos países, lo que puede resultar especialmente beneficioso para los productos que se venden tanto en Estados Unidos como en Canadá.
Marcas UL vs. cUL: El etiquetado de las certificaciones UL y cUL difiere para indicar el mercado específico para el que se ha certificado el producto. Un producto certificado para el mercado estadounidense llevará la marca UL, mientras que un producto certificado para Canadá mostrará la marca cUL. Esta distinción es fundamental para garantizar que los productos sean fácilmente identificables como compatibles con las normas nacionales correspondientes.
Existe la idea errónea de que los productos con certificación CSA solo se pueden usar en Canadá y no se pueden vender ni instalar en los EE. UU., mientras que los productos con certificación UL se pueden usar en los Estados Unidos y en todo el mundo. Según la certificación, tanto los productos CSA como los UL se pueden usar a nivel local e internacional.
5. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre UL Listed y UL Recognized?
Las marcas UL Listed y UL Recognized son indicadores de certificación proporcionados por Underwriters Laboratories (UL), una empresa global de consultoría y certificación de seguridad. Estas marcas significan que un producto o componente ha cumplido con estándares de seguridad específicos, pero se aplican a diferentes tipos de productos y cumplen propósitos distintos en los mercados de fabricación y consumo.
La certificación UL Listed se aplica a productos independientes y totalmente funcionales que han sido probados y han demostrado que cumplen con los estándares de seguridad necesarios para un uso específico previsto. Esta marca se encuentra comúnmente en productos para el usuario final, como electrodomésticos, dispositivos electrónicos y equipos industriales. La marca UL Listed garantiza a los consumidores, minoristas y autoridades regulatorias que el producto es seguro para su uso y cumple con todos los requisitos de seguridad pertinentes. Los productos con esta certificación han sido sometidos a una evaluación exhaustiva, que incluye pruebas de incendio, descarga eléctrica y otros peligros potenciales.
Por otro lado, la certificación UL Recognized se aplica a componentes o materiales destinados a ser utilizados dentro de un sistema o producto más grande. Estos pueden incluir piezas como placas de circuitos, fuentes de alimentación, plásticos o cableado. La marca UL Recognized indica que el componente cumple con ciertas normas de seguridad, pero puede requerir una evaluación adicional cuando se integra en un producto final. Esta certificación es particularmente importante para los fabricantes e integradores de sistemas, ya que les ayuda a seleccionar componentes confiables y que cumplan con las normas durante el proceso de desarrollo del producto. El uso de componentes UL Recognized puede agilizar el proceso de certificación del producto final, pero el producto completo aún deberá someterse a su propia evaluación para lograr el estado UL Listed.
6. ¿Qué es la certificación CSA?
CSA Group (anteriormente Canadian Standards Association) es una organización líder en Canadá encargada de desarrollar normas y certificar productos para garantizar que cumplan con los requisitos de seguridad, salud y medio ambiente. La certificación CSA es esencial para los productos destinados al mercado canadiense, en particular para dispositivos eléctricos y electrónicos, electrodomésticos y equipos industriales.
Marca CSA: La marca CSA es un símbolo muy reconocido en Canadá que indica que un producto ha sido probado y certificado exhaustivamente para cumplir con estándares específicos de seguridad y rendimiento. En el caso de los productos eléctricos, la certificación CSA garantiza que el artículo cumple con el Código Eléctrico Canadiense y otras normas pertinentes, lo que reduce el riesgo de incendios eléctricos, descargas eléctricas y otros peligros.
Reconocimiento global: La certificación CSA no solo es reconocida en Canadá, sino que también tiene un peso significativo a nivel internacional. Muchos países e industrias consideran que los productos con certificación CSA son confiables y seguros, lo que puede mejorar la comercialización de un producto fuera de Canadá. Este reconocimiento global permite a los fabricantes con productos con certificación CSA expandir su alcance a los mercados internacionales con mayor confianza.
Preferencia de mercado: En algunos casos, los consumidores y los reguladores canadienses pueden preferir los productos certificados por la CSA porque el Grupo CSA es una organización local con profundas raíces en las normas de seguridad canadienses. Sin embargo, ambas certificaciones son aceptables para la mayoría de los propósitos regulatorios y los fabricantes pueden elegir la que mejor se adapte a su estrategia de mercado.
7. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre CSA y cUL?
Tanto las certificaciones CSA como cUL indican el cumplimiento de las normas de seguridad canadienses, pero son emitidas por organizaciones diferentes. La certificación CSA la otorga el Grupo CSA, mientras que la certificación cUL la emite Underwriters Laboratories para productos que cumplen con las normas canadienses. Aunque ambas certificaciones son respetadas en Canadá, la CSA suele considerarse la certificación más tradicional y reconocida localmente, mientras que la cUL forma parte del sistema UL más amplio, que también cubre el mercado estadounidense.
8. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre CSA y UL?
Tanto la CSA como la UL son laboratorios de pruebas reconocidos a nivel nacional (NRTL, por sus siglas en inglés) que prueban la seguridad y eficacia de ciertos tipos de productos. De hecho, la certificación de la CSA y la certificación de la UL son prácticamente sinónimos. Ambas organizaciones están acreditadas por la OSHA (Administración de Seguridad y Salud Ocupacional) y el ANSI (Instituto Nacional Estadounidense de Normas) para actuar como NRTL.
Ambas empresas, CSA y UL, firmaron un Memorando de Entendimiento que define la aceptación mutua de pruebas e investigaciones de acuerdo con estándares definidos.
En definitiva, CSA y UL son simplemente dos organizaciones diferentes que realizan pruebas según el mismo conjunto de estándares. En cualquier caso, un producto certificado a través de uno de estos NRTL cumple con los estándares de la industria en materia de seguridad y rendimiento.
El acuerdo de memorando de entendimiento entre ambas organizaciones simplifica el proceso de certificación para las empresas que deseen obtener las marcas estadounidenses y/o canadienses. Si una empresa requiere la marca CSA o UL, puede solicitar la aprobación de la CSA (Canadian Standards Association) o de la UL (Underwriters Laboratories Inc.).
9. ¿Qué es NRTL?
Un NRTL (pronunciado “nurtle”) es un laboratorio de pruebas reconocido a nivel nacional acreditado por la Administración de Seguridad y Salud Ocupacional (OSHA) como certificador aprobado de estándares industriales específicos. La acreditación de OSHA como NRTL garantiza que una organización cumple con los requisitos de 29 CFR 1910.7. Cada NRTL está acreditado por OSHA para un alcance particular de estándares de prueba y tiene su propia marca de certificación registrada única, que un fabricante está autorizado a colocar en un producto certificado.
Si un fabricante planea vender o distribuir equipos eléctricos en los Estados Unidos, debe demostrar que su producto es seguro. Esto se hace obteniendo la certificación a través de un laboratorio de pruebas reconocido a nivel nacional aprobado por la OSHA.
El NRTL puede probar el producto eléctrico en cuestión según una norma nacional específica, lo que demuestra que el producto cumple con los requisitos para venderse en los Estados Unidos. Una vez aprobado, el NRTL autoriza al fabricante a aplicar la marca NRTL a toda la producción futura de la fábrica. La única diferencia entre las distintas marcas NRTL radica en los servicios de los laboratorios de pruebas que las respaldan.
10. ¿Qué es ETL?
La certificación ETL funciona como UL en el sentido de que también proporciona un sello de que un producto es sólido y cumple con los estándares establecidos.
ETL es un laboratorio de pruebas con sede en Londres, especializado en diversos tipos de pruebas, entre ellas, pruebas de rendimiento comparativo, compatibilidad electromagnética y seguridad de productos para electrónica. Fundada por Thomas Edison en 1896, ETL tiene una larga trayectoria en la garantía de que los productos cumplen con los estándares de seguridad y rendimiento. La organización opera actualmente más de 30 oficinas y laboratorios en todo el mundo, adhiriéndose a los mismos principios que Edison estableció, centrándose en la seguridad de productos, materiales y componentes patentados. Era una empresa que solía llamarse "Edison Testing Laboratories".
11. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre ETL y UL?
Las marcas registradas de ETL y las marcas de UL tienen similitudes en el sentido de que ambas se derivan de pruebas certificadas por NRTL para garantizar que los productos electrónicos sean seguros para el uso público. Sin embargo, ambos métodos de prueba difieren en las metodologías de prueba y los parámetros de referencia que determinan la seguridad del producto.
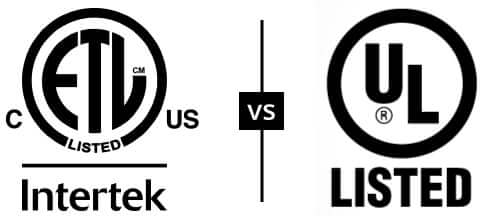
La certificación ETL también es válida principalmente en América del Norte. Sin embargo, una diferencia importante entre UL y ETL es que esta última tiene un atractivo global un poco más amplio.
Una marca ETL verificada con un identificador “US” en la posición de las 4 en punto significa que el producto ha sido identificado como que cumple únicamente con los estándares de seguridad de EE. UU., según lo define el Título 29 CRF.
Se ha determinado que una marca verificada por ETL con una “C” en la posición de las 8 en punto cumple únicamente con los estándares de seguridad de productos canadienses. Los productos que llevan tanto “US” como “C” cumplen con los estándares de seguridad de productos de EE. UU. y Canadá.
12. ¿Qué son las normas NEMA?
La Asociación Nacional de Fabricantes Eléctricos (NEMA) es una organización influyente que desarrolla estándares para productos eléctricos, incluidas las clasificaciones para gabinetes eléctricos, interruptores y otros equipos utilizados en una variedad de entornos. Los estándares NEMA se utilizan ampliamente en los EE. UU. y son esenciales para garantizar la seguridad y confiabilidad de los sistemas eléctricos tanto en entornos residenciales como industriales.
Clasificaciones NEMA: Las clasificaciones NEMA son un aspecto fundamental de las normas, ya que especifican el nivel de protección que ofrece un gabinete eléctrico contra factores ambientales como polvo, agua, productos químicos e impacto físico. Por ejemplo, un gabinete NEMA 4 está diseñado para uso en interiores y exteriores y brinda protección contra la entrada de agua proveniente de la lluvia, el aguanieve y el agua arrojada por mangueras. Las clasificaciones más altas, como NEMA 6P, indican protección contra la inmersión en agua y la exposición a agentes corrosivos.
13. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre NEMA y UL?
La Asociación Nacional de Fabricantes Eléctricos (NEMA) y Underwriters Laboratories (UL) son las dos agencias reguladoras a las que se hace referencia comúnmente en América del Norte. Ambas brindan supervisión para garantizar que un gabinete cumpla o supere un determinado grado de protección. Ambas definen los diseños de gabinetes, contra qué contaminantes puede brindar protección cada diseño y cómo se prueba cada diseño para garantizar el cumplimiento con su respectiva clasificación o tipo.
La diferencia más importante entre los gabinetes con clasificación NEMA y los de tipo UL es cómo se realizan las pruebas y el proceso de cumplimiento. Los gabinetes con clasificación NEMA están certificados por el propio fabricante.
14. ¿Qué son las normas ASTM?
ASTM International, anteriormente conocida como la Sociedad Estadounidense de Pruebas y Materiales, es un líder reconocido mundialmente en el desarrollo y la entrega de estándares de consenso voluntarios. Estos estándares cubren una amplia gama de materiales, productos, sistemas y servicios, con el objetivo de garantizar la calidad, la seguridad y el rendimiento en diversas industrias.
Alcance y aplicación: Las normas ASTM se utilizan en todo el mundo para mejorar la calidad de los productos, aumentar la seguridad, facilitar el acceso al mercado y el comercio, y generar confianza en los consumidores. Abarcan una amplia gama de industrias, entre ellas la construcción, el petróleo, los textiles y los productos de consumo. En el contexto de los conductos eléctricos, las normas ASTM garantizan que los materiales como el PVC utilizado en la fabricación de conductos cumplan con criterios específicos de durabilidad, resistencia química y otras características de rendimiento.
Impacto global: las normas ASTM suelen ser referenciadas por otras organizaciones de normalización y organismos reguladores a nivel mundial, lo que las hace esenciales para los fabricantes que buscan garantizar que sus productos cumplan con los parámetros de referencia internacionales. El cumplimiento de las normas ASTM también puede facilitar el ingreso al mercado, ya que es más probable que los productos sean aceptados en múltiples regiones.
15. ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la norma ASTM y UL?
Tanto Underwriters Laboratories (UL) como ASTM International son fundamentales para mantener altos estándares en diversas industrias, pero sus funciones y áreas de enfoque son distintas. UL se especializa en pruebas y certificación de seguridad de productos. Desarrolla estándares de seguridad rigurosos para una amplia gama de categorías de productos, incluidos equipos eléctricos y bienes de consumo. El objetivo principal de UL es garantizar que los productos sean seguros para su uso mediante el establecimiento de criterios de rendimiento y la realización de pruebas e inspecciones exhaustivas. Los productos que cumplen con estos criterios reciben la marca UL, que indica el cumplimiento de estrictos requisitos de seguridad.
ASTM International, por otro lado, es reconocida por crear estándares de consenso voluntarios que se centran en las especificaciones técnicas y las características de desempeño de materiales, productos y sistemas. A diferencia de UL, ASTM no ofrece servicios de certificación, sino que proporciona pautas y metodologías detalladas para evaluar la calidad y la consistencia de los productos. Los estándares de ASTM cubren un amplio espectro de industrias, incluidas la construcción, la energía y la fabricación. Estos estándares tienen como objetivo garantizar que los productos y materiales cumplan con parámetros de desempeño específicos, promoviendo la confiabilidad y la interoperabilidad.
Las diferencias en el alcance y los procesos de certificación entre UL y ASTM resaltan sus roles únicos. Las normas de UL se ocupan principalmente de la seguridad, abordando los peligros potenciales y asegurando que los productos cumplan con criterios de seguridad integrales. En contraste, las normas de ASTM enfatizan los aspectos técnicos y de rendimiento en lugar de la certificación de seguridad. El proceso de certificación de UL implica pruebas rigurosas y auditorías periódicas para garantizar el cumplimiento continuo, mientras que ASTM proporciona pautas que los fabricantes utilizan para el control de calidad interno y el desarrollo de productos. Comprender estas diferencias permite a las empresas navegar de manera efectiva por las normas relevantes para sus productos e industrias. Diferencias entre ASTM y otros laboratorios de la misma manera, como CSA, ETL, etc.
16. ¿Cuál es el papel del NEC (Código Eléctrico Nacional)?
El Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC), también conocido como NFPA 70, es un conjunto de pautas vitales en los Estados Unidos que regulan la instalación segura de cableado y equipos eléctricos. Fue desarrollado por la Asociación Nacional de Protección contra Incendios (NFPA) y se adoptó ampliamente en todo Estados Unidos como estándar para garantizar la seguridad eléctrica en edificios residenciales, comerciales e industriales.
Cumplimiento del NEC: el cumplimiento del NEC es obligatorio para todas las instalaciones eléctricas en los EE. UU. El código cubre todo, desde la instalación correcta de conductos y cables hasta la conexión a tierra y la unión, la protección de circuitos y más. El cumplimiento de las pautas del NEC es crucial para prevenir incendios eléctricos, reducir el riesgo de descarga eléctrica y garantizar la seguridad general de los sistemas eléctricos.
Influencia global: si bien el NEC es específico de los Estados Unidos, su influencia se extiende más allá de las fronteras estadounidenses. Muchos otros países y regiones consideran al NEC como modelo para sus códigos eléctricos y adoptan normas similares para garantizar la seguridad y la confiabilidad de sus instalaciones eléctricas.
17. ¿Cuál es el papel del CEC (Código Eléctrico Canadiense)?
El Código Eléctrico Canadiense (CEC) es un conjunto integral de normas y reglamentos diseñados para garantizar la instalación, el funcionamiento y el mantenimiento seguros de los sistemas eléctricos en Canadá. Desarrollado por la Asociación Canadiense de Normas (CSA), el CEC establece los requisitos mínimos de seguridad eléctrica en entornos residenciales, comerciales e industriales. Abarca una amplia gama de temas, incluidos los métodos de cableado, la conexión a tierra, las especificaciones de los equipos y la instalación de dispositivos eléctricos.
El CEC se actualiza periódicamente para reflejar los avances en la tecnología, los cambios en las prácticas de seguridad y las nuevas necesidades de la industria. El cumplimiento del CEC es obligatorio en todo Canadá y el código suele adoptarse en las leyes provinciales y territoriales, lo que lo convierte en un requisito legal para todos los trabajos eléctricos. Está diseñado para proteger tanto al público como a los trabajadores eléctricos de peligros eléctricos como descargas eléctricas, incendios y explosiones.
Si bien el CEC comparte muchas similitudes con el Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC) de los EE. UU., existen diferencias específicas que reflejan el entorno regulatorio y los estándares de seguridad únicos de Canadá. Estas diferencias significan que las instalaciones eléctricas que cumplen con un código pueden no cumplir completamente con los requisitos del otro; la correlación de los requisitos técnicos entre los dos códigos está en curso.
18. ¿Qué es la certificación CE?
La marca CE es una marca de conformidad obligatoria para los productos que se venden en el Espacio Económico Europeo (EEE). Significa que un producto cumple con los requisitos esenciales de la legislación europea pertinente en materia de salud, seguridad y protección del medio ambiente, que están diseñados para garantizar la seguridad del consumidor y promover el libre comercio dentro del EEE.
Alcance del marcado CE: El marcado CE se aplica a una amplia gama de productos, incluidos equipos eléctricos, dispositivos médicos, maquinaria y productos de construcción. En el caso de los productos eléctricos, el marcado CE indica el cumplimiento de directivas como la Directiva de baja tensión (LVD) y la Directiva de compatibilidad electromagnética (EMC), que cubren cuestiones de seguridad e interferencias electromagnéticas.
Cumplimiento: Para colocar la marca CE, los fabricantes deben asegurarse de que sus productos cumplen todas las directivas y normas aplicables de la UE. Este proceso suele implicar pruebas rigurosas, documentación y, en algunos casos, certificación de terceros, según la categoría del producto y los riesgos asociados. La marca CE no solo facilita el libre comercio dentro del EEE, sino que también sirve como garantía para los consumidores de que el producto cumple con altos estándares de seguridad y calidad.
Acceso al mercado: La marca CE es esencial para los fabricantes que desean vender sus productos en el mercado europeo. Sin ella, los productos no pueden comercializarse legalmente dentro del EEE, lo que podría limitar el potencial de crecimiento de una empresa. Además, la marca CE está reconocida en algunos países no pertenecientes a la UE, que pueden aceptarla como prueba de cumplimiento de sus propias normas de seguridad.
19. ¿Qué son las normas IEC?
La Comisión Electrotécnica Internacional (IEC) es una organización reconocida mundialmente que desarrolla estándares internacionales para tecnologías eléctricas, electrónicas y afines. Los estándares IEC tienen como objetivo garantizar la seguridad, compatibilidad y eficiencia de los productos en todo el mundo, facilitando el comercio internacional y la innovación en las industrias eléctricas y electrónicas.
Normas globales: las normas IEC son adoptadas por muchos países de todo el mundo y proporcionan un marco coherente para el diseño, las pruebas y el rendimiento de los productos eléctricos. Esta armonización de normas ayuda a los fabricantes a reducir el coste y la complejidad de sacar nuevos productos al mercado, ya que elimina la necesidad de contar con múltiples certificaciones específicas de cada país.
Relevancia para la industria: Para los fabricantes, cumplir con las normas IEC es crucial para garantizar que sus productos puedan competir en el mercado global. Los productos que cumplen con las normas IEC suelen ser aceptados en múltiples mercados sin necesidad de certificación adicional, lo que agiliza el proceso de aprobación y acelera el tiempo de comercialización. Además, las normas IEC contribuyen a la confiabilidad y seguridad generales de los sistemas eléctricos en todo el mundo, lo que promueve la confianza de los consumidores y el crecimiento de la industria.
20. ¿Qué es ISO?
La Organización Internacional de Normalización (ISO) es una entidad global no gubernamental fundada en 1947 y con sede en Ginebra, Suiza. Su función principal es desarrollar y publicar una amplia gama de normas que abarcan diversos sectores, desde la atención sanitaria y la tecnología hasta la fabricación y la gestión medioambiental. Las normas de la ISO tienen como objetivo garantizar que los productos, servicios y sistemas sean seguros, fiables y de alta calidad, facilitando así el comercio internacional y fomentando la coherencia entre fronteras.
Entre las normas ISO más importantes se encuentran la ISO 9001, que se centra en los sistemas de gestión de la calidad, y la ISO 14001, que aborda la gestión medioambiental. Las normas ISO son fundamentales para garantizar la seguridad, la fiabilidad y la calidad en diversas aplicaciones. Los esfuerzos de la ISO en materia de normalización ayudan a agilizar el comercio mundial al proporcionar un marco común para evaluar y mantener la calidad de los productos y servicios.
21. ¿Qué es la norma AS/NZS?
Las normas AS/NZS son un conjunto de normas técnicas desarrolladas conjuntamente por Standards Australia (AS) y Standards New Zealand (NZS). Estas normas están diseñadas para garantizar la seguridad, la fiabilidad y la eficiencia de los productos, servicios y sistemas en Australia y Nueva Zelanda. Las normas AS/NZS abarcan una amplia gama de áreas, entre las que se incluyen la construcción, la ingeniería, la tecnología de la información, la gestión medioambiental y los bienes de consumo.
La colaboración entre Standards Australia y Standards New Zealand comenzó a principios de los años 90 con el objetivo de armonizar las normas entre ambos países. Esta iniciativa surgió del deseo de facilitar el comercio, mejorar la seguridad de los productos y reducir las barreras regulatorias. A lo largo de los años, la asociación ha dado como resultado el desarrollo de numerosas normas conjuntas que son reconocidas y adoptadas en ambos países.
La norma AS/NZS 2053 especifica los requisitos para los conductos y accesorios metálicos y no metálicos utilizados en instalaciones eléctricas en estas regiones. Esta norma garantiza que los conductos y accesorios proporcionen la protección adecuada para los cables eléctricos y cumplan con los requisitos ambientales y de seguridad específicos de Australia y Nueva Zelanda.
La norma AS/NZS 2053 cubre diversos aspectos del rendimiento de los conductos, incluida la resistencia del material, la resistencia a factores ambientales (como la radiación ultravioleta, los productos químicos y las temperaturas extremas) y la facilidad de instalación. También aborda las propiedades mecánicas de los conductos, como la resistencia al impacto y la flexibilidad, lo que garantiza que puedan soportar los rigores de la instalación y el uso a largo plazo.
Ctube es un reconocido fabricante y proveedor de conductos, tuberías y accesorios de PVC, especializado en brindar soluciones innovadoras para proyectos de construcción. Tiene su sede en China.
Hemos obtenido las certificaciones ISO 9001, ISO 14001 e ISO 45001, lo que garantiza a nuestros clientes los más altos estándares en control de calidad y prácticas ambientalmente sostenibles. Además, nuestros productos cuentan con certificaciones internacionales como UL, CSA, AS/NZS 2053, CE e IEC, lo que valida aún más su confiabilidad y cumplimiento.
Si tiene requisitos de proyecto, comuníquese con nosotros.