1. Introducción
Think of PVC conduit as the protective tunnel for your electrical cables — just like how a well-built subway keeps trains safe and running smoothly underground.
If the tunnel is built poorly, trains might slow down or get stuck.
Similarly, if PVC conduit is installed incorrectly, it can lead to problems like damaged wires, safety risks, and costly repairs.
If you’re planning to install PVC conduit for your electrical wiring project, this post may be helpful.
Some common mistakes include poor planning, choosing the wrong conduit size, overfilling the conduit, too many bends, using the wrong fittings, ignoring environmental factors, poor sealing, especially outdoors or underground, improper cutting, failing to secure the conduit, neglecting electrical codes, and not planning for future expansion.
In this post, we’ll walk through the most frequent slip-ups people encounter when installing PVC conduit.
Whether you’re a seasoned electrician, a DIY enthusiast, or someone just starting to learn about electrical installations, understanding the common mistakes people make with PVC conduit can save you a lot of time and money.
2. Poor Planning Before Installation
Here’s a truth that many people learn the hard way: jumping into PVC conduit installation without a clear plan is like setting off on a road trip without a map or GPS — you might get somewhere, but it probably won’t be the right place, and you’ll waste a lot of time and energy along the way.

Poor planning can lead to all kinds of headaches: wasted materials, having to redo work, unexpected obstacles on site, or even safety hazards.
For example, without a proper layout plan, you might end up with conduits running in awkward directions, too many bends, or unnecessary lengths that increase both cost and complexity.
So what does good planning look like? Start by sketching a simple conduit route on paper or with digital tools. Think about where your cables need to go, any obstacles you’ll have to work around, and how to minimize bends (each bend makes pulling cable harder). Also, consider future expansion — it’s smart to plan for any additional wiring you might add later.
Many of the mistakes we’re about to introduce stem primarily from a lack of proper planning. One common example is choosing the wrong conduit size — a seemingly small decision that can cause big problems later on.
3. Choosing the Wrong Conduit Size
Picking the right size of PVC conduit might seem straightforward, but it’s one of the easiest mistakes to make.
Imagine trying to squeeze a big group of people through a narrow hallway. It’s going to be uncomfortable, slow, and maybe even unsafe, right?
The same goes for your electrical cables inside the conduit.
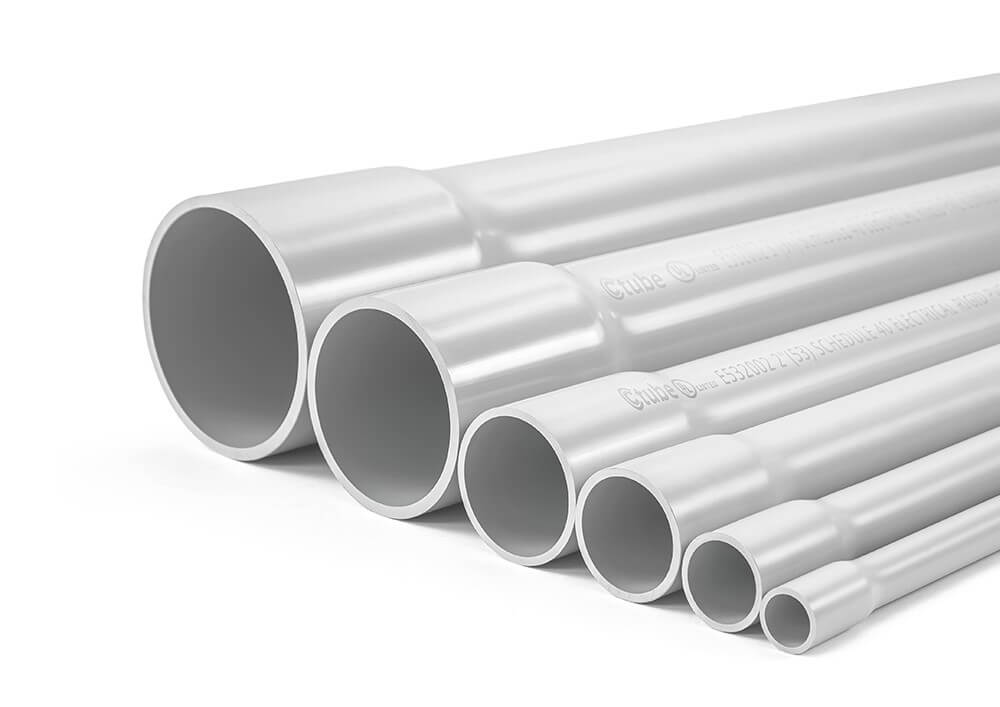

If your conduit is too small, the cables get cramped, making it harder to pull them through, and they can overheat because there’s less space for heat to escape.
On the other hand, if you go too big, you’ll end up wasting materials and space — kind of like buying a jumbo suitcase when a carry-on would do.
So, how do you get it right? The National Electrical Code (NEC) usually recommends filling no more than 40% of the conduit’s internal area to keep things safe and manageable.
Before buying or cutting any pipes, take some time to calculate the total diameter of your cables and choose a conduit size that fits comfortably. A little planning here will save you from pulling your hair out later!
👉 If you want to know more about the conduit size choosing, this post may be helpful Cómo elegir el tamaño del conducto para instalaciones eléctricas.
4. Overfilling the Conduit
We talked earlier about the importance of choosing the right conduit size — and now, let’s take that one step further. Even if you’ve selected the correct diameter, overfilling the conduit is still a common pitfall that can lead to serious problems if not handled properly.
Imagine trying to shove too many clothes into a suitcase — it bulges, the zipper strains, and you just know something’s going to rip. PVC conduit works the same way. When it’s overfilled with too many wires or cables, you put your entire system at risk.
Overfilling is one of the most common — and most overlooked — mistakes in electrical conduit installations. It may not seem like a big deal at first, but cramming too many conductors inside a conduit can lead to:
- Overheating
- Increased friction during pulling
- Difficulty in future maintenance or upgrades
- Non-compliance with electrical codes like the NEC
The National Electrical Code (NEC) has strict rules about conduit fill capacity.
For example, if you’re using three or more conductors, the total cross-sectional area of all cables must not exceed 40% of the internal area of the conduit as we have mentioned above.
Sounds a little technical? Don’t worry — there are charts and tools to help.
📘 If you are interested in diving deeper into how to calculate PVC conduit fill properly, here we provide a post Guía completa sobre las tablas de llenado de conductos de PVC (2025) that explains everything in detail for you — checking out if you want to get the numbers just right!
5. Avoiding Excessive Bends
When planning your PVC conduit installation, one of the most important things to pay attention to is how you handle bends and turns.
Think of your conduit like a smooth highway for your cables. If the highway has too many sharp turns or twists, traffic will slow down, and accidents are more likely.
Similarly, too many bends in your conduit make it much harder to pull cables through, and could even damage them.

According to electrical standards like the NEC (National Electrical Code), the number of bends between pull points should not exceed 360 degrees total. This usually means you can have up to four 90-degree bends or their equivalent.
If your conduit path requires more than this, you must install a pull box or junction box at strategic points. These boxes give you access to change direction safely and make cable pulling manageable — like rest stops on that winding highway.
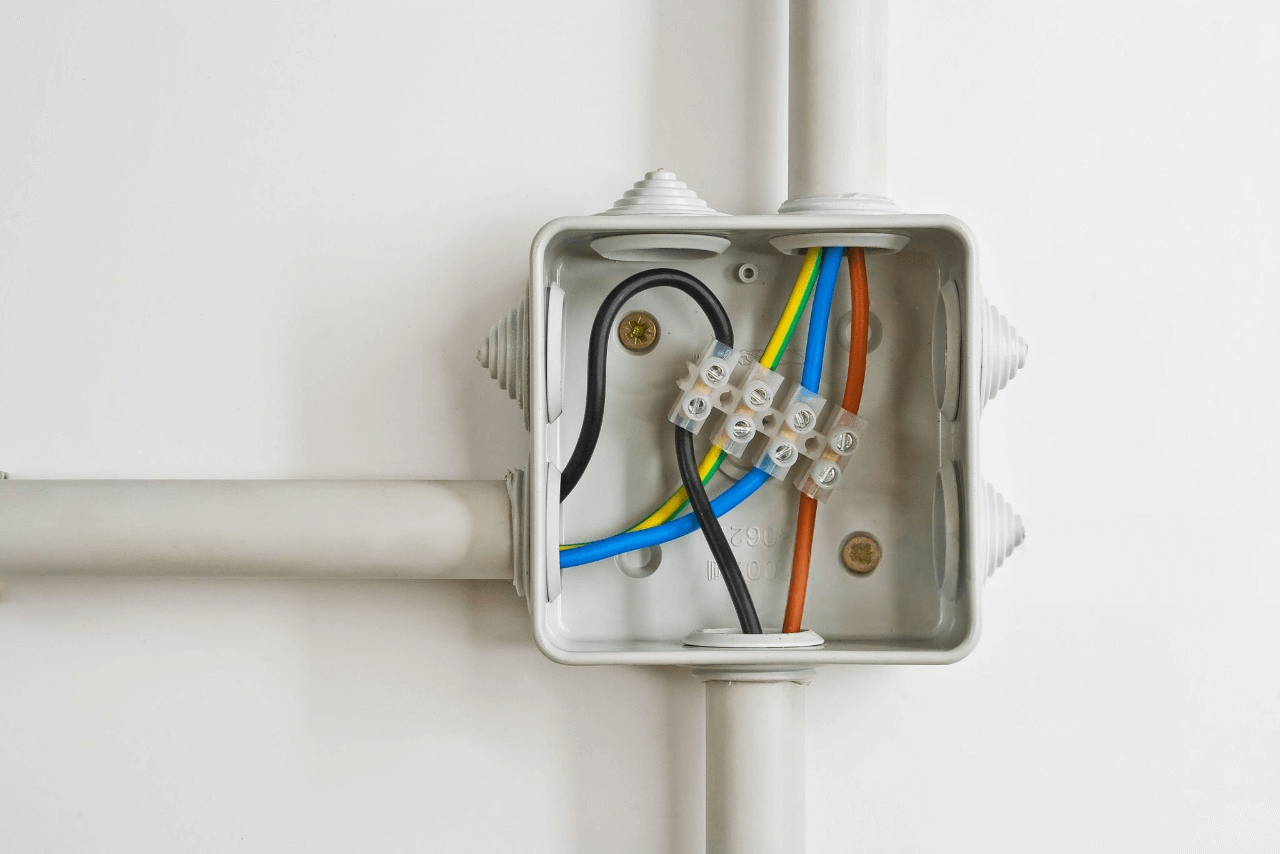
Also, the NEC advises using long-radius bends instead of sharp 90-degree angles whenever possible. Long-radius bends give cables more room to curve gently, reducing strain and making installation smoother.
6. Using Incorrect Fittings or Accessories
Using the wrong fitting is a bit like wearing the wrong size of shoes — it might get you through the day, but it’s going to be uncomfortable, and eventually, something’s going to break.
The same goes for PVC conduit installations. Fittings are the key to connecting and securing your system, and choosing the wrong type or size can lead to loose connections, water leaks, or even code violations.
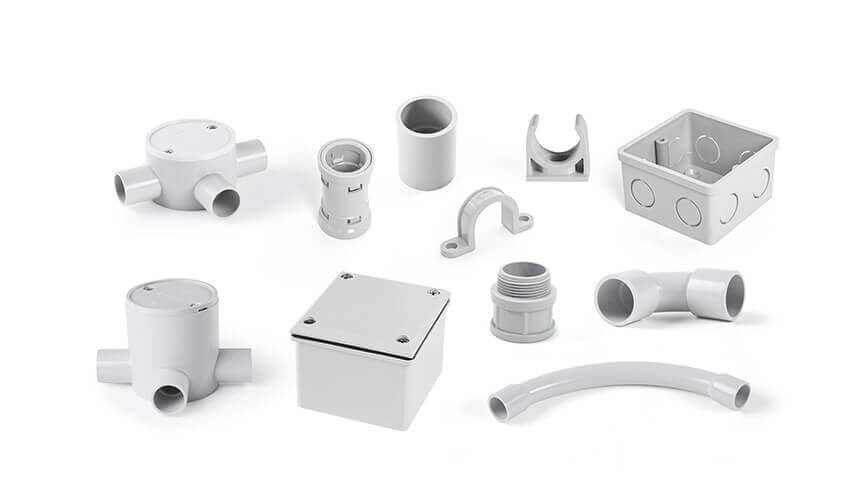

Wrong size match: Just because two parts seem to “fit” doesn’t mean they’re the same size. Using a fitting that’s too tight or too loose can compromise the entire system. Always match the fitting size to the conduit diameter exactly.
Mismatched types: Electrical PVC conduit fittings are different from plumbing fittings, even if they look similar. Using a plumbing elbow or coupling in an electrical application is a common but critical mistake — electrical fittings are designed for wire pulling and code compliance.
Improper transition fittings: When connecting PVC conduit to metal boxes or other materials, it’s important to use the correct male adapters, threaded connectors, or transition couplings to maintain grounding and mechanical integrity.
Skipping box connectors or locknuts: When entering a junction box or enclosure, you should always use box connectors and secure them properly with locknuts. Otherwise, the conduit might shift or disconnect over time.
📌If you’re curious about which fittings can actually make your installation faster and smarter, we’ve also put together a helpful guide 6 innovadores accesorios para conductos de PVC que aumentan la eficiencia.
7. Ignoring Environmental Factors
When installing PVC conduit, one common mistake is overlooking the environment where the conduit will live.
🌳Think of it like planting a tree—you wouldn’t plant a delicate tropical tree in the middle of a snowy tundra and expect it to thrive, right? The same idea applies here.
Environmental factors such as temperature extremes, UV exposure, moisture, soil type, and even chemical exposure can all affect how well your PVC conduit performs and lasts.
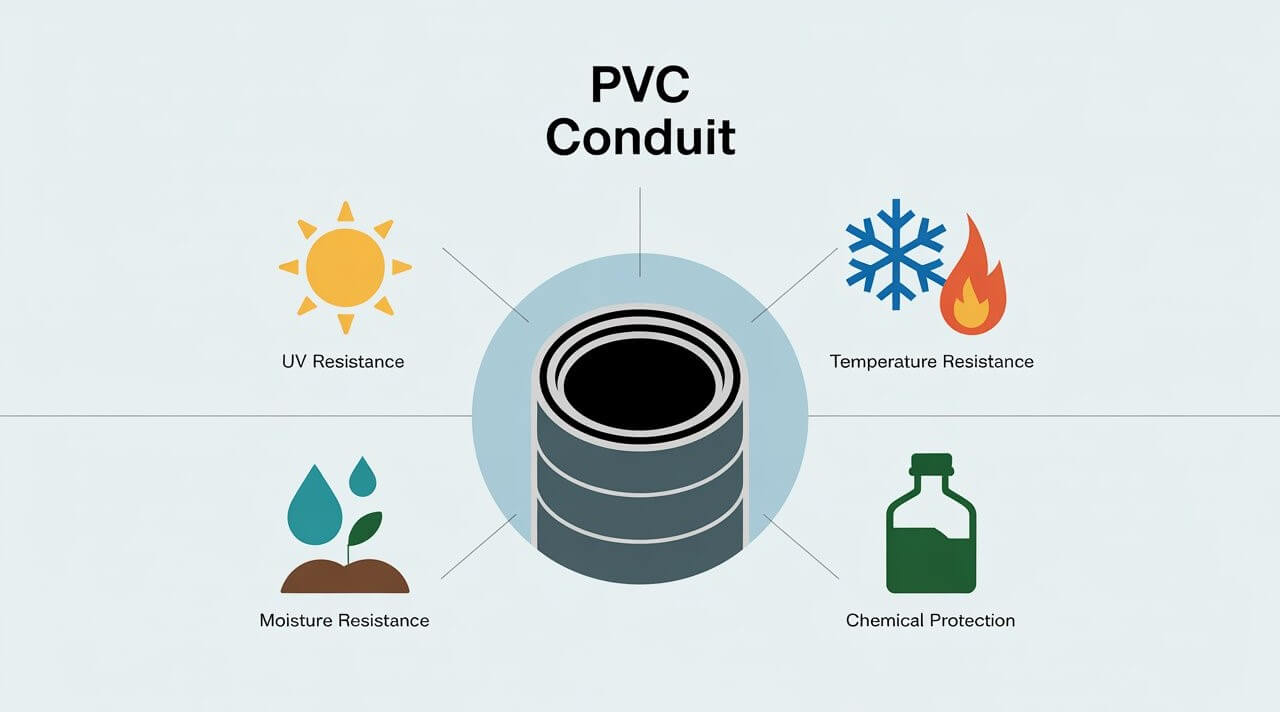
🌞 UV Exposure: Prolonged sunlight can degrade some types of PVC conduit, making it brittle over time. If your installation is outdoors, choose UV-resistant conduit or consider painting it with a UV-protective coating.
❄️ Temperaturas extremas: PVC can become brittle in very cold weather or soften in extreme heat. Make sure to select conduit rated for the temperature range of your location.
💧 Moisture and Soil Conditions: Underground conduit faces moisture, soil acidity, and shifting soil. Proper sealing, burial depth, and choosing conduits designed for direct burial are crucial.
⚗️ Chemical Exposure: Some industrial sites or agricultural settings have chemicals in soil or water that can degrade PVC. Always verify that your conduit material is resistant to any chemicals it might encounter.
Ignoring these factors might lead to premature cracking, leaks, or system failures. So, take the time to assess the environment and choose the right materials and installation methods — your conduit will thank you later!
8. Poor Sealing for Outdoor or Underground Use
Installing PVC conduit pipe outdoors or underground? Then sealing isn’t just a good idea — it’s essential. Think of it like building a tent in the rain 🌧️.
If you don’t close up every flap and seam, water will find a way in. And just like that soggy sleeping bag, your conduit and wiring could suffer.
Many people overlook this step or assume the conduit will naturally be waterproof once it’s connected.
Unfortunately, that’s not the case.
Water, dirt, insects, and even plant roots can sneak into unsealed joints or entry points, leading to corrosion of conductors, short circuits, or degraded insulation over time.
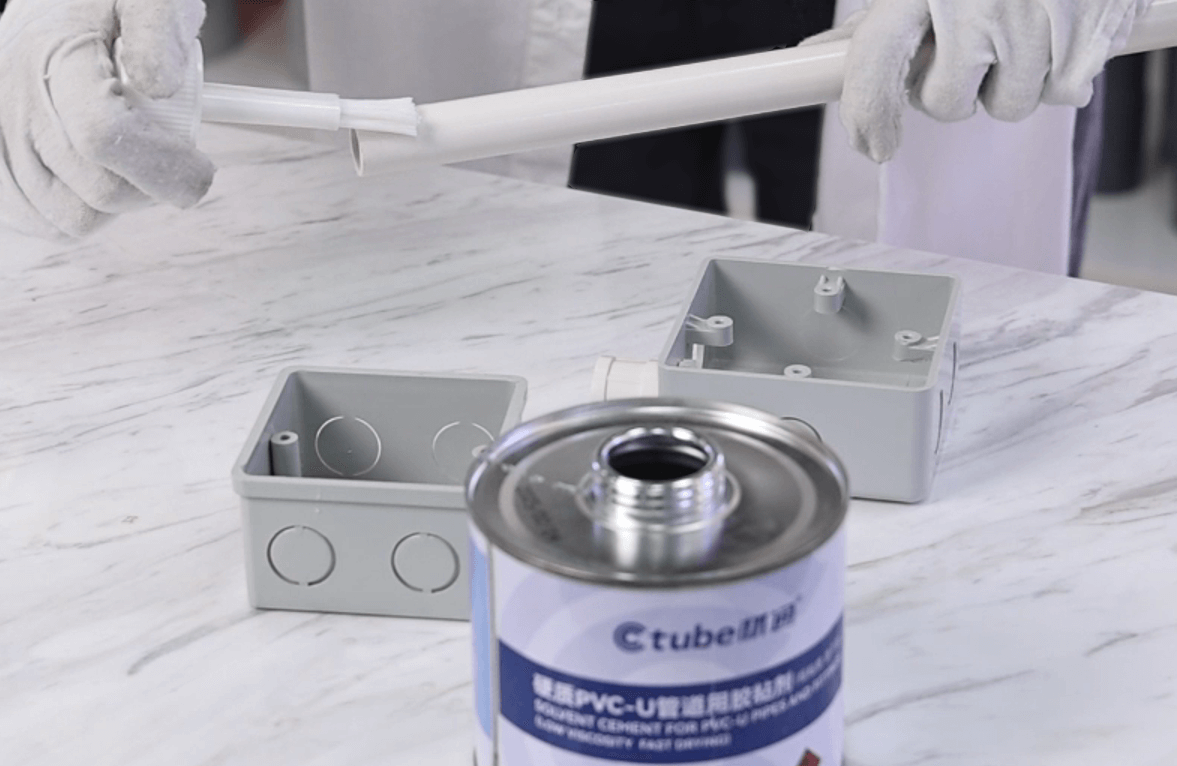

So what should you do?
✅ Use approved solvent cement to seal joints completely, proper solvent cementing is one key part of sealing, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle.
✅ Apply watertight fittings like gaskets, bushings, and weatherproof connectors, especially where the conduit enters an enclosure or box.
✅ Seal entry points into buildings or underground boxes with weatherproof sealant or expandable foam.
✅ Use expansion fittings if temperature changes are expected, especially in outdoor runs — this prevents gaps from forming when conduit expands or contracts.
📌 Pro tip: For underground installations, always follow NEC and local code requirements for burial depth and backfilling — and double-check that your conduit ends are completely sealed before covering them up!
9. Improper Cutting and Deburring
Cutting PVC electrical conduit might seem like a simple task — just slice and go, right? But improper cutting and deburring can cause more trouble than you’d expect.
Imagine trying to push a delicate cable through a conduit with rough, jagged edges inside — it’s like trying to slide a smooth ribbon through a rough keyhole. Those sharp edges can snag, damage, or even wear down the cable insulation over time, leading to shorts or failures down the road.
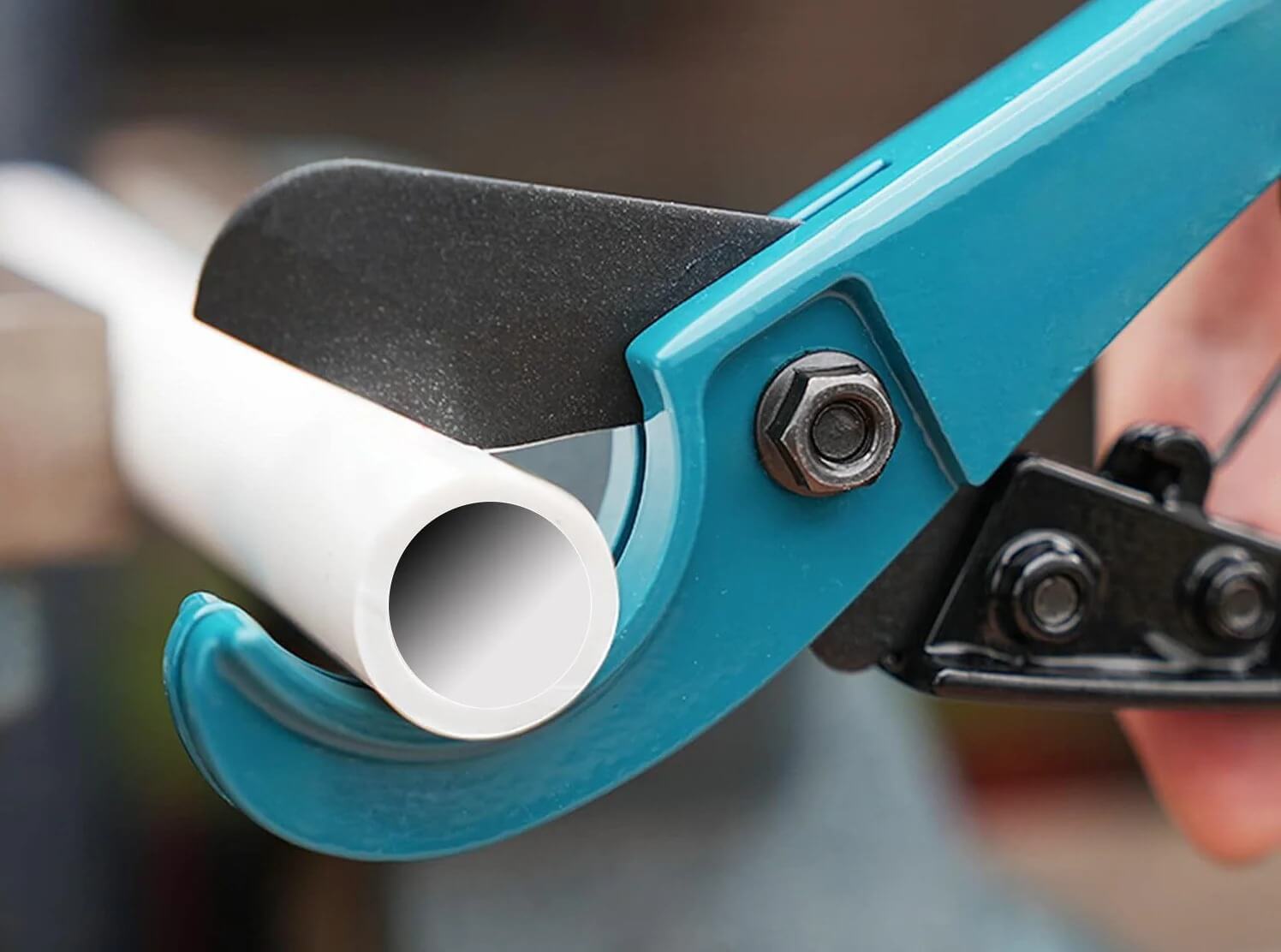

So, how to do it right?
✅ Use a proper PVC conduit cutter or a fine-toothed hacksaw for clean, straight cuts.
✅ After cutting, always deburr the inside and outside edges using a reaming tool, a round file, or sandpaper — smooth edges help cables glide through easily.
✅ Take your time and check each cut before installation to avoid surprises later.
📝 Here we provide a post A Step-by-Step Guide How to Cut PVC Conduit that explains conduit cutting in detail for you.
10. Mistakes During Underground Installation
Before we dive into the specific challenges of underground PVC conduit installation, let’s quickly recall a few important points we’ve already touched on — like the critical role of proper sealing to keep moisture and dirt out, the use of expansion fittings to accommodate temperature changes and prevent gaps, and the strategic placement of pull boxes to make cable pulling easier and avoid excessive bends.
These elements lay a solid foundation for a durable and trouble-free underground conduit system. However, underground installations come with their own unique challenges and potential pitfalls that we should be aware of.

✅ Incorrect Burial Depth
One of the most common mistakes is not following the required burial depth. According to the NEC (National Electrical Code), the minimum burial depth for rigid nonmetallic conduit (PVC) in most residential applications is 18 inches.
However, this can vary depending on factors like voltage, location (driveway, lawn, or under a building).

✅ Skipping Conduit Markers or Warning Tape
Underground conduits are easy to forget once buried — until someone accidentally digs them up! This tape acts as a bright, early alert for anyone digging in the future.
Lay a continuous warning tape about 12 inches above the conduit to avoid accidental damage later.

✅ Improper Backfilling
Improper backfill can crush or crack PVC conduit, especially under pressure from vehicles or heavy soil.
Use soft fill material like sand or clean soil around and over the conduit first. Compact it in layers to avoid shifting, then finish with your usual fill.
11. Failing to Secure Conduit
Imagine trying to build a house without nails or screws — no matter how well you line things up, they won’t stay in place for long.
The same logic applies to PVC conduit: if it’s not properly secured, your entire electrical system could suffer.
Improperly secured conduit can sag, shift, disconnect at the joints, or place stress on fittings and enclosures.
Over time, this not only looks messy but can also lead to cable damage, compromised seals, or violations of building codes.
To avoid this, always follow spacing guidelines set by the National Electrical Code (NEC).
For example, smaller-diameter PVC conduit may require support every 3 feet, while larger sizes may allow wider spacing — but only if the material remains stable and straight.
And finally, choose support materials that are appropriate for the environment. In outdoor or corrosive settings, consider UV-resistant or corrosion-resistant clips and anchors.
12. Neglecting Electrical Codes and Regulations
Throughout this guide, we’ve mentioned how important it is to follow the NEC — the National Electrical Code — and there’s a good reason for that.
If you skip over code requirements or assume they don’t apply, you’re taking a big risk. Mistakes like the wrong burial depth, incorrect conduit size, or poor sealing could all lead to fire hazards, shock risks, or expensive do-overs — and you may even fail inspection.
Every country, and sometimes even different cities or regions, may have their own electrical rules. It’s important to check what’s required in your area before starting any installation. Whether it’s NEC in the U.S., AS/NZS standards in Australia and New Zealand, or local codes elsewhere, all of them exist for one goal: safety and reliability.
So before you pick up your tools, double-check the codes. Following the rules from the start is always easier (and cheaper) than fixing a mistake later.
13. Not Planning for Future Expansion
Earlier, we talked about the importance of choosing the right conduit size and planning your layout before installation. One key reason for that is often overlooked: future expansion.
Electrical systems rarely stay the same forever. Whether it’s adding new equipment, outlets, or lighting, chances are you’ll need to run more cables down the road. If your conduits are already full, you might face major headaches — like tearing everything out just to add a few wires.
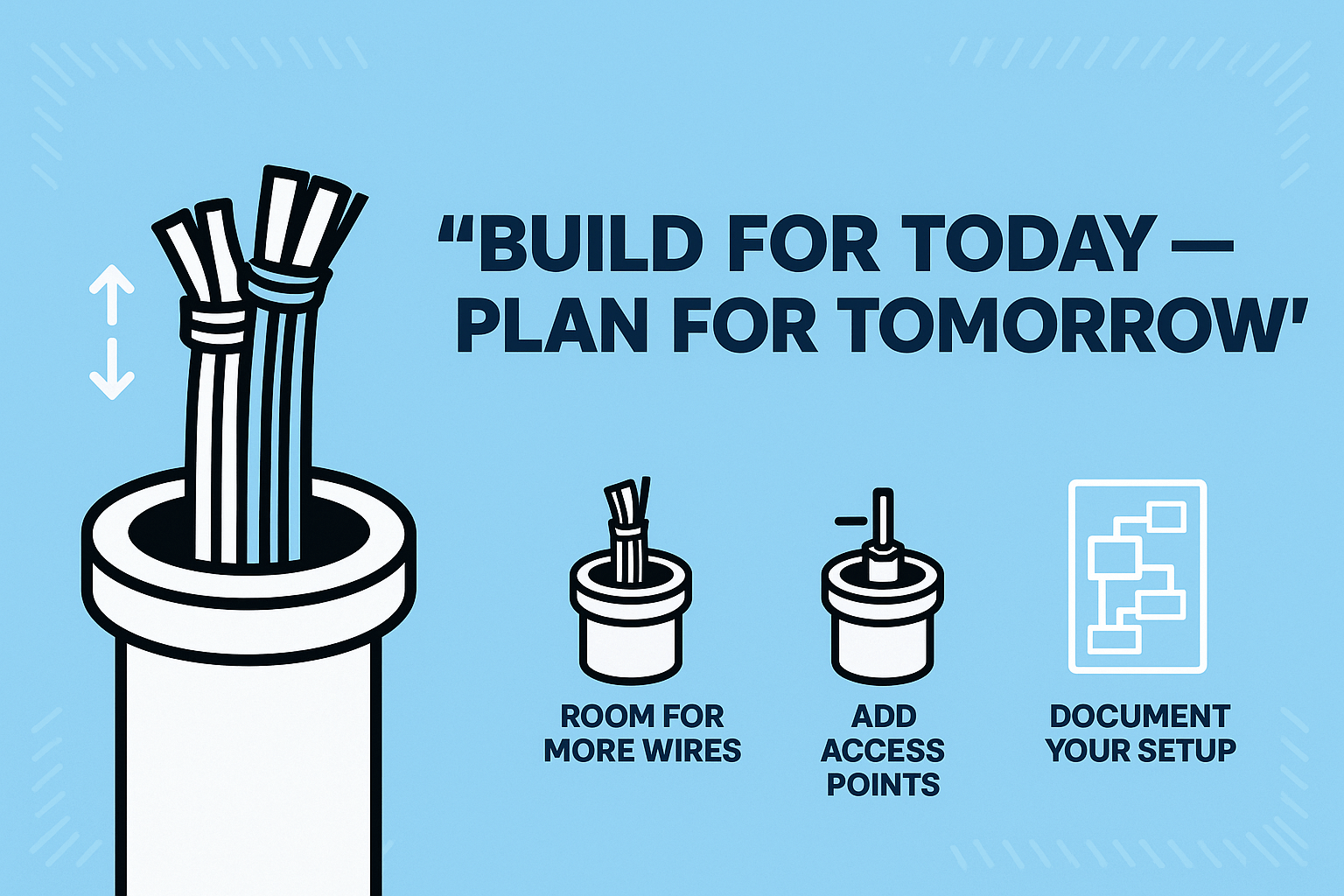
What’s the smart move?
✅ Choose a conduit size that allows room for future cable runs — not just what you need today.
✅ Leave access points or junction boxes where new circuits could easily tie in.
✅ Document your layout clearly so future upgrades won’t be a guessing game.
A little foresight now can save a lot of time, money, and hassle later. Think of it as building not just for today — but for tomorrow too.
14. Conclusion
Installing PVC conduit might seem simple, but as we’ve seen, even small mistakes can lead to big problems later — from water damage and overheating to failed inspections or expensive rework.
The good news is, most of these issues can be avoided with good planning, attention to detail, and by following safety standards like the NEC.

En Ctube, we’re here to help you do the job right from the start. We offer a wide range of high-quality PVC conduits and fittings that meet international standards, including underground-rated products, weather-resistant options, and solutions for both commercial and residential needs.
🎯 Want to learn more about electrical conduit, installation tips, and the latest industry updates?
📩 Follow Ctube on LinkedIn or other social media like Facebook or Instagram or YouTube, we regularly share helpful information about PVC conduit, fittings, and best practices for electrical projects — whether you’re a contractor, engineer, or just planning your next project.
📚 Read more helpful post from our blog pages to learn more about electrical conduit.
Thank you for reading. We hope this article has been helpful in guiding your conduit selection.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to contact us. We wish you great success with your project!