What is the Difference Between Cables and Conduits
1 المقدمة
When working on an electrical project, it’s common to see cables and conduits purchased together. In fact, many contractors and buyers treat them as a package — one carries the wires, the other protects them. But while they’re often used side by side, cables and conduits are actually very different products.
A cable is a complete wiring system, with conductors and insulation bundled together. A conduit, on the other hand, is an empty protective tube designed to hold and guide individual wires. They serve different roles, follow different installation methods, and are even classified differently in building codes.
Understanding the difference between these two is important — not just for proper installation, but for choosing the right material, meeting code requirements, and ensuring long-term safety.
In this post, we’ll introduce what cables and conduits are, how they compare, and when to use each one.
2. What is an Electrical Cable?
An electrical cable is a group of wires bundled together and protected by insulation. It’s designed to carry electricity from one point to another — for example, from a breaker panel to outlets, switches, or light fixtures. Most cables are ready to install right out of the box, which makes them a convenient choice for many residential and light commercial projects.
Cables usually contain two or more conductors, each covered with colored insulation to show their purpose (like black for hot, white for neutral, and green or bare for ground). These wires are then wrapped in a non-metallic sheath or a metallic armor, depending on the cable type. The outer jacket protects the wires from damage during and after installation.
Some of the most common types of electrical cable include:
- NM (Non-Metallic) Cable, also known as Romex, used widely in residential indoor wiring.
- Armored Cable (AC or BX), which has a metal casing for extra protection, often used in commercial buildings.
- Flexible Cord, used for appliances or temporary connections.
Cables are typically installed inside walls, ceilings, or floors, where they’re protected from physical damage. In many cases — especially in residential settings — they can be used without conduit, as long as local codes allow.
Because they come pre-assembled and don’t require pulling individual wires through tubing, electrical cables are faster to install and generally more cost-effective than conduit systems. However, they may not provide the same level of mechanical protection or flexibility when changes or expansions are needed — and that’s where conduit comes in.
3. What is a Conduit?
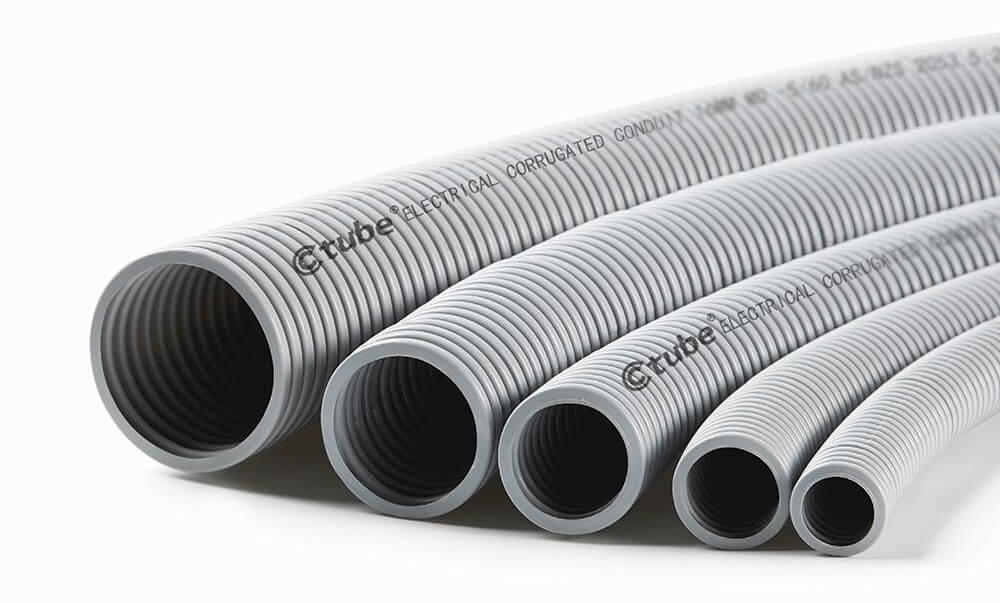
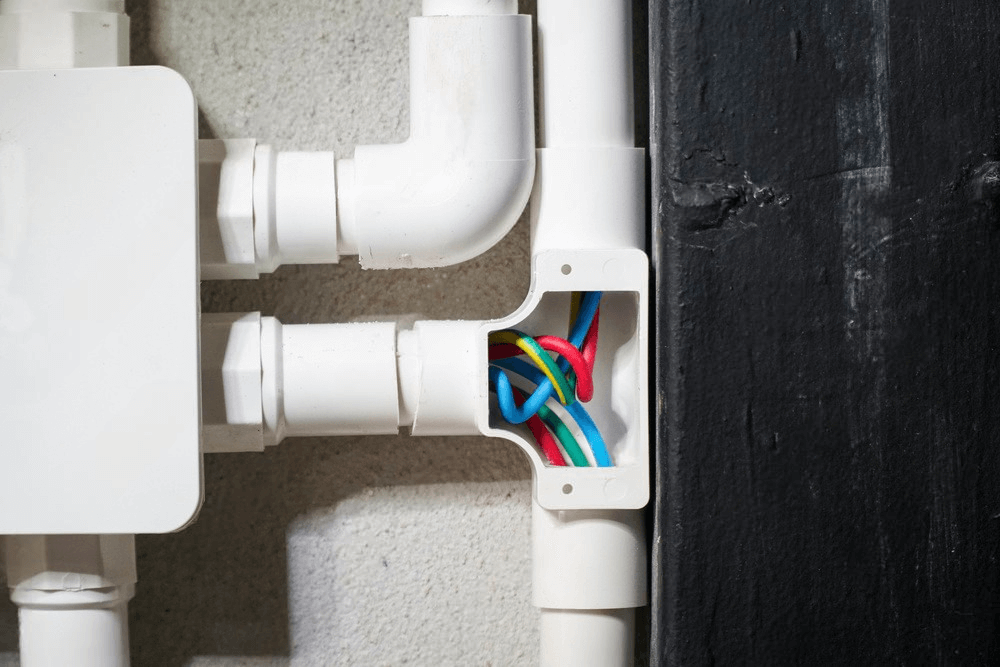
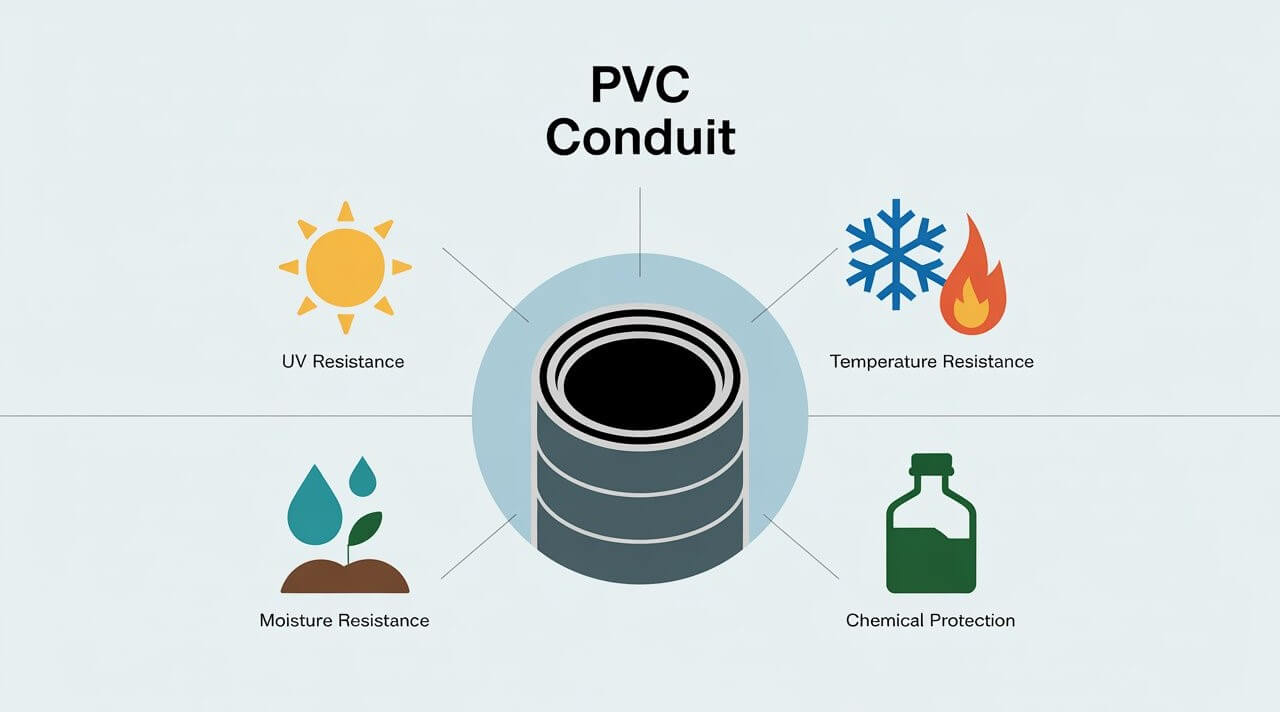
A conduit is a hollow tube used to protect and route individual electrical wires. Unlike a cable, which comes with wires already bundled inside, a conduit is empty — wires are pulled through it during installation. This setup offers more flexibility and stronger protection, especially in environments where wiring is exposed to moisture, impact, or heat.
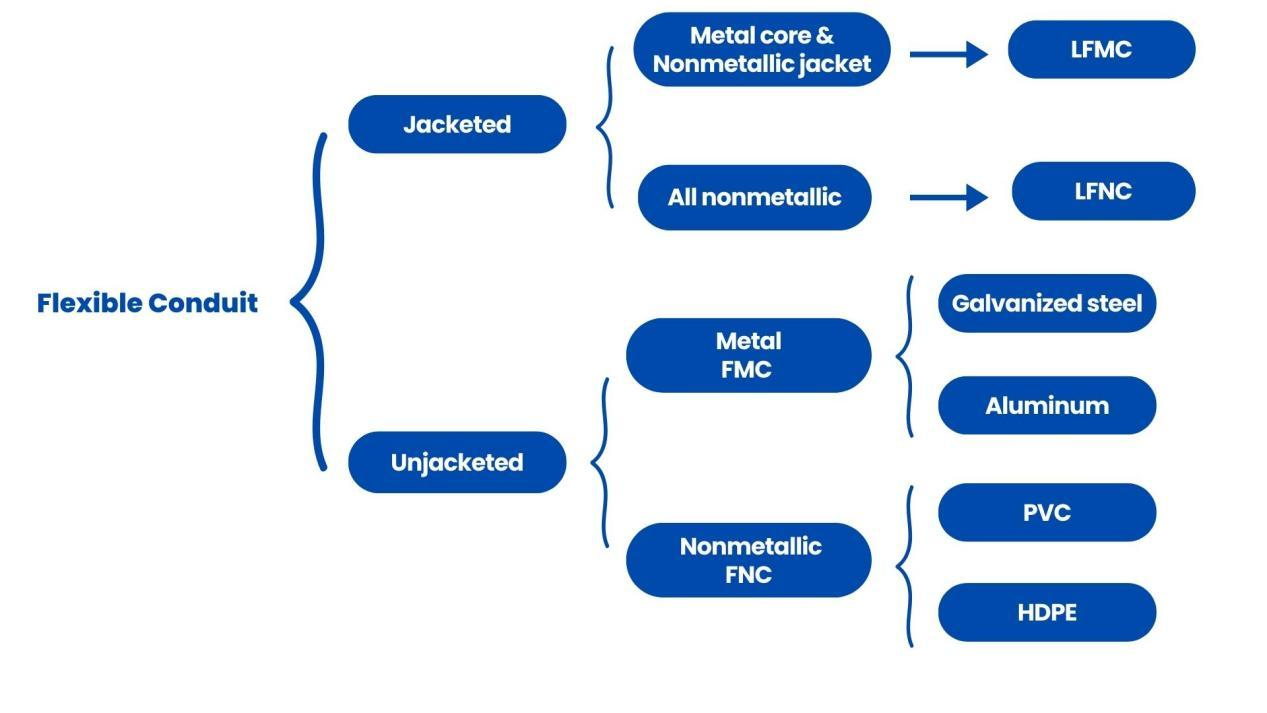
📦 Materials of Conduits
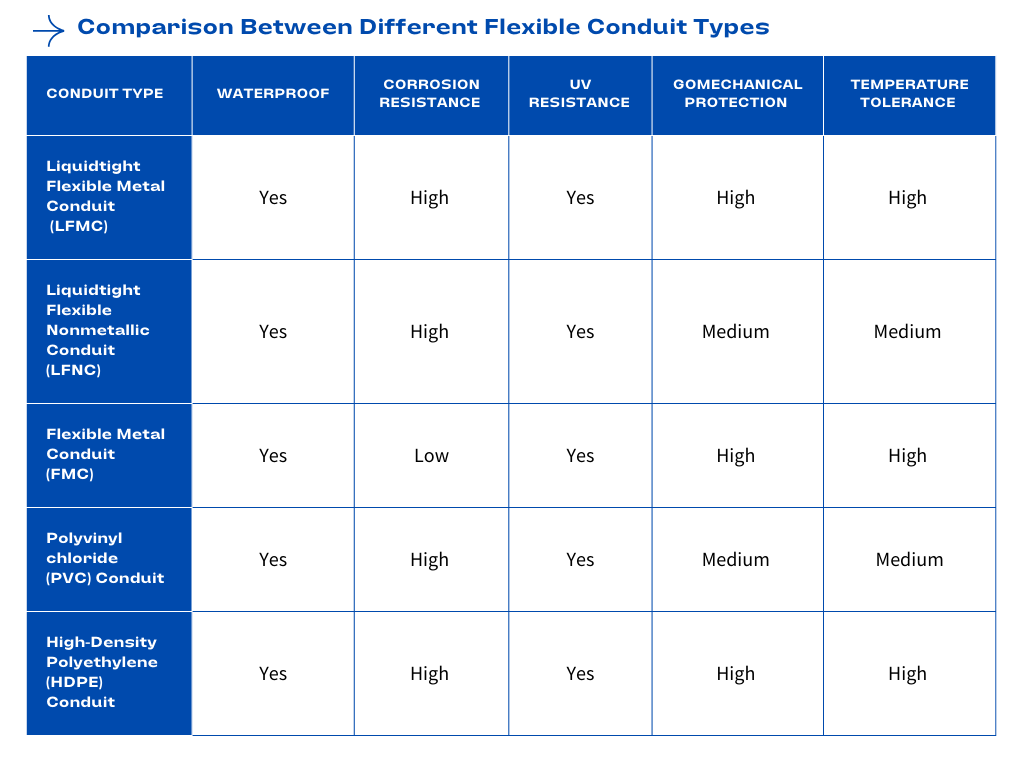
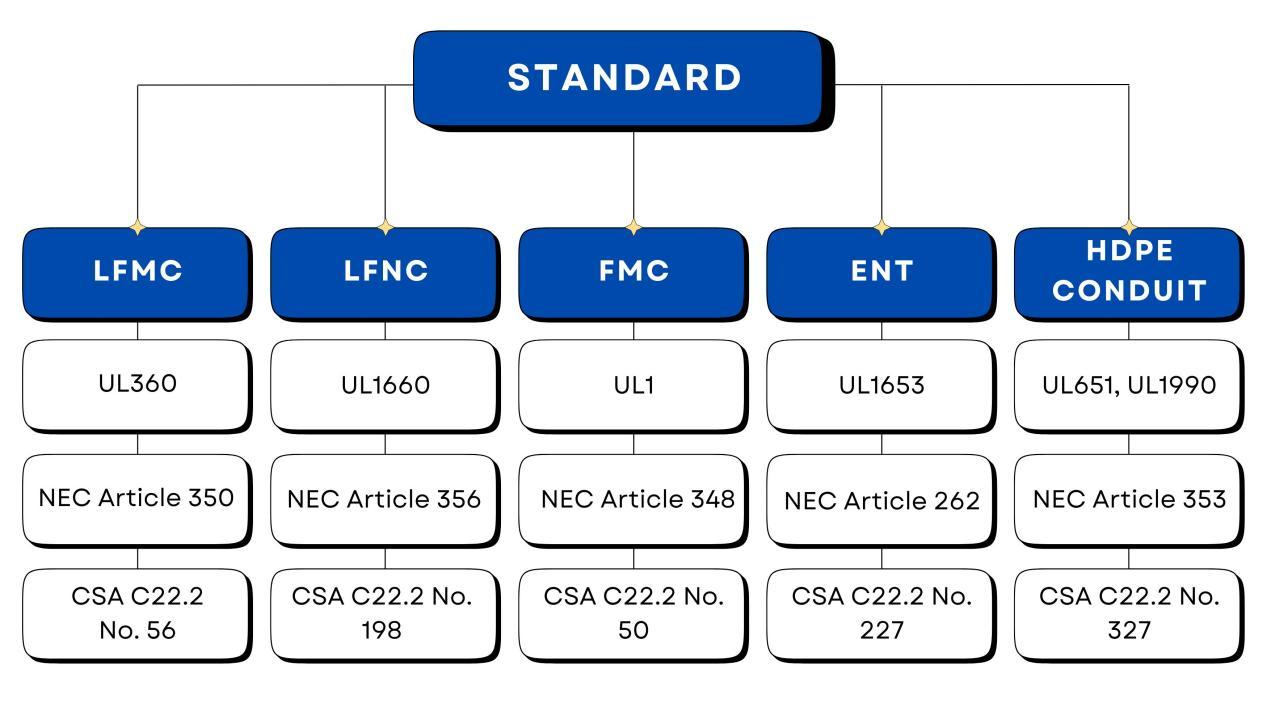
Conduits come in a wide range of materials, chosen based on the environment, installation method, and code requirements. The two broad categories are:
🔹 Non-metallic Conduits
- بولي فينيل كلوريد (PVC) – Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, commonly used in residential, underground, and wet locations.
- RTRC – Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit (fiberglass); ideal for corrosive or high-temperature environments.
- البولي ايثيلين عالي الكثافة – High-Density Polyethylene; flexible, used mostly for directional boring or underground installs.
- Composite Types – Combine metallic core with non-metallic jacket for strength and corrosion resistance.
🔹 Metallic Conduits
- طب الطوارئ – Electrical Metallic Tubing; lightweight steel, used for indoor commercial wiring.
- RMC – Rigid Metal Conduit; thick-walled and highly protective.
- آي إم سي – Intermediate Metal Conduit; lighter than RMC but still strong.
- FMC – Flexible Metal Conduit; bends easily, ideal for equipment connections or tight spots.
🌀 Rigid vs. Flexible Conduits
- مواسير صلبة – Maintain fixed shape; offer robust protection for structured layouts.
- الأنابيب المرنة – Designed to bend; useful around corners, equipment, or obstacles.
Choosing the right conduit type depends on location (indoor vs. outdoor), exposure to moisture or impact, ease of installation, and need for future changes or flexibility.
4. Key Differences Between Cable and Conduit
Although cables and conduits are often used together, they are fundamentally different in how they’re built, installed, and used.
Here’s a clear breakdown of the key differences between the two:
| ميزة | كابل | Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Structure | A complete unit with insulated wires bundled together | An empty tube that houses individual wires |
| تثبيت | Simple and fast; just run and secure the cable | Requires pulling wires through conduit; more labor-intensive |
| مادة | Usually plastic-sheathed (e.g., NM cable), or armored metal | Can be metal (EMT, RMC) or non-metal (PVC, RTRC, HDPE) |
| المرونة | Pre-assembled; less flexible in design changes | Allows easier rewiring or additions later |
| الحماية الميكانيكية | Limited; cable sheath offers basic protection | High; especially in rigid or metal conduit types |
| متطلبات الكود | Allowed in many indoor residential settings | Often required in commercial, industrial, outdoor, or wet areas |
| يكلف | Lower material and labor cost | Higher cost, but offers longer-term flexibility and safety |
| Typical Use | Indoor residential wiring (walls, ceilings, floors) | Outdoor, underground, exposed wiring, or commercial buildings |
💡 Choosing the Right One
Use cable when you need a fast, low-cost installation in a dry, protected indoor environment — like behind drywall in a house.
Use conduit when the wiring is exposed, underground, in a corrosive or wet environment, or in a setting where future upgrades may be needed.
Local electrical codes (such as the NEC in the U.S.) often dictate which method is required, depending on the location and purpose of the wiring. Understanding these differences not only helps ensure a safe and code-compliant installation — it also helps you choose the most efficient and cost-effective solution for your project.
5. When to Use Cable vs. Conduit?
For wiring inside finished walls, ceilings, or floors in most homes, non-metallic cable (NM cable, also known as Romex) is a practical and widely accepted choice. It’s fast to install, cost-effective, and fully compliant with code in dry, enclosed indoor spaces. That’s why it’s commonly used in bedrooms, living rooms, hallways, and similar areas.
In this type of environment, cable offers enough protection and keeps installation simple — especially when running wires through wood framing during construction or renovation.
However, if you’re planning for the long term — such as future smart home upgrades or possible layout changes — installing conduit instead of cable in key routes can give you more flexibility later. Some homeowners also prefer conduit for peace of mind, knowing the wires are better protected inside a sealed pathway.
These days, there are many residential-friendly conduit options that are lightweight, easy to cut, and designed for indoor use. So while cable is typically enough for most home interiors, conduit is worth considering if you’re thinking ahead, or simply want a more durable solution.
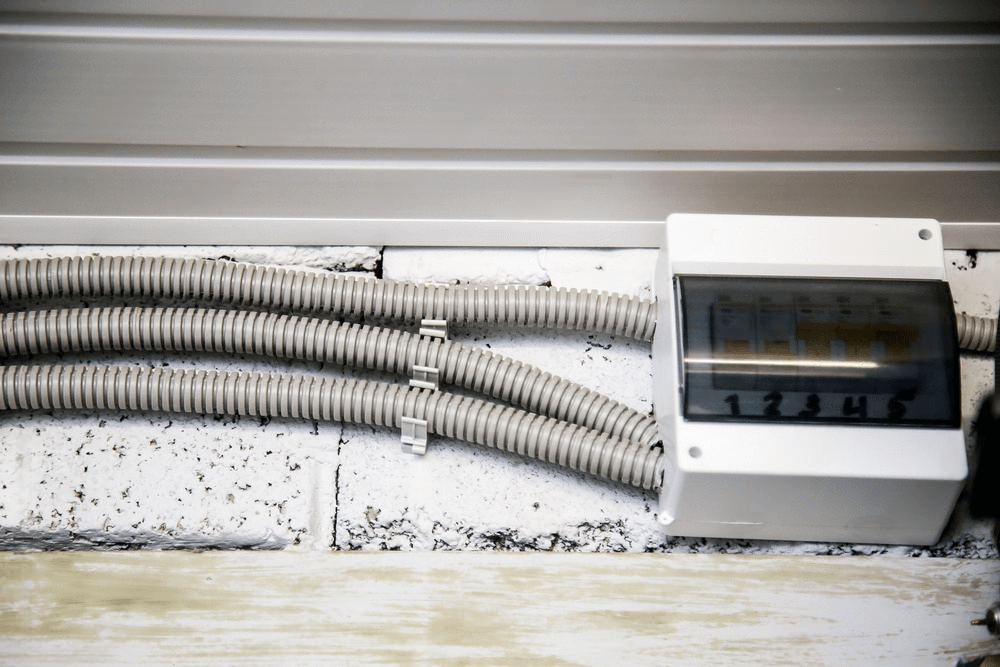
In unfinished or semi-exposed areas like garages, basements, laundry rooms, and utility spaces, using conduit is often the safer and more reliable choice. These spaces are more likely to experience moisture, temperature changes, and accidental contact with stored items, tools, or vehicles. In such environments, cable alone may not provide enough protection, and local electrical codes often reflect that.
Conduit — whether it’s PVC, EMT (metal), or flexible types — helps protect wires from physical damage, dampness, and even rodents. For example, in a garage where bikes, ladders, or garden tools are constantly moved around, exposed cable could easily get snagged or crushed. Conduit creates a sealed pathway around the wires, making the system more durable and secure.
Another benefit of using conduit in these areas is a cleaner, more organized appearance, especially if the wiring is surface-mounted. Instead of having loose cables stapled along walls or ceilings, conduit keeps everything neat and professional-looking — which is especially appreciated in finished basements or multi-use garage spaces.
While conduit takes a bit more time to install than cable, in these specific parts of a home, it often pays off in long-term reliability and code compliance.
In commercial settings — like offices, shops, restaurants, schools, and public buildings — conduit is almost always the standard for electrical installations. These environments demand higher levels of safety, durability, and long-term flexibility, which cable systems alone often can’t provide.
Conduit is often required by code in commercial projects, especially when wiring is exposed or runs through areas where it might be damaged. But beyond code compliance, conduit brings real practical benefits: it keeps wiring organized, allows easy upgrades, and maintains a professional, finished appearance — all of which matter in a busy workspace.
In open-ceiling designs (common in modern offices or retail spaces), conduit also serves a visual function, guiding cables neatly across beams or walls. It can be painted to match the interior or grouped together for a clean look.
Because commercial spaces often change over time — adding new equipment, lighting, or systems — using conduit from the beginning makes future changes much easier. Wires can be pulled in or out as needed, without damaging finished surfaces.
So while conduit might take more planning and labor upfront, in commercial and office spaces, it’s the smart and expected choice.
When wiring needs to run outside a building or underground, using conduit isn’t just a good idea — it’s usually required. These environments expose electrical wiring to moisture, sunlight, physical damage, corrosion, and shifting soil — all of which can quickly degrade unprotected cable.
In most cases, PVC conduit is the go-to choice for underground installations. It’s corrosion-resistant, lightweight, and approved for direct burial when properly sealed. For more demanding underground work, like long runs or trenchless boring, HDPE conduit may be used thanks to its flexibility and impact resistance. In exposed outdoor areas, such as rooftops or exterior walls, rigid metal conduit (RMC) or weather-rated PVC is often used for its strength and durability.
Unlike cable, which cannot be buried or exposed unless specially rated and protected, conduit systems create a sealed, physical barrier that shields wires from moisture and environmental damage. It also helps prevent accidental contact with the wiring — a major safety factor in outdoor or public spaces.
Even for short outdoor runs — like connecting a garage, garden light, or pool pump — it’s important to use conduit to meet code and protect the installation over time. Skipping conduit in these conditions can lead to faster failure, unsafe wiring, and expensive repairs later.
In short: when wiring leaves the building, it needs more protection — and conduit provides exactly that.
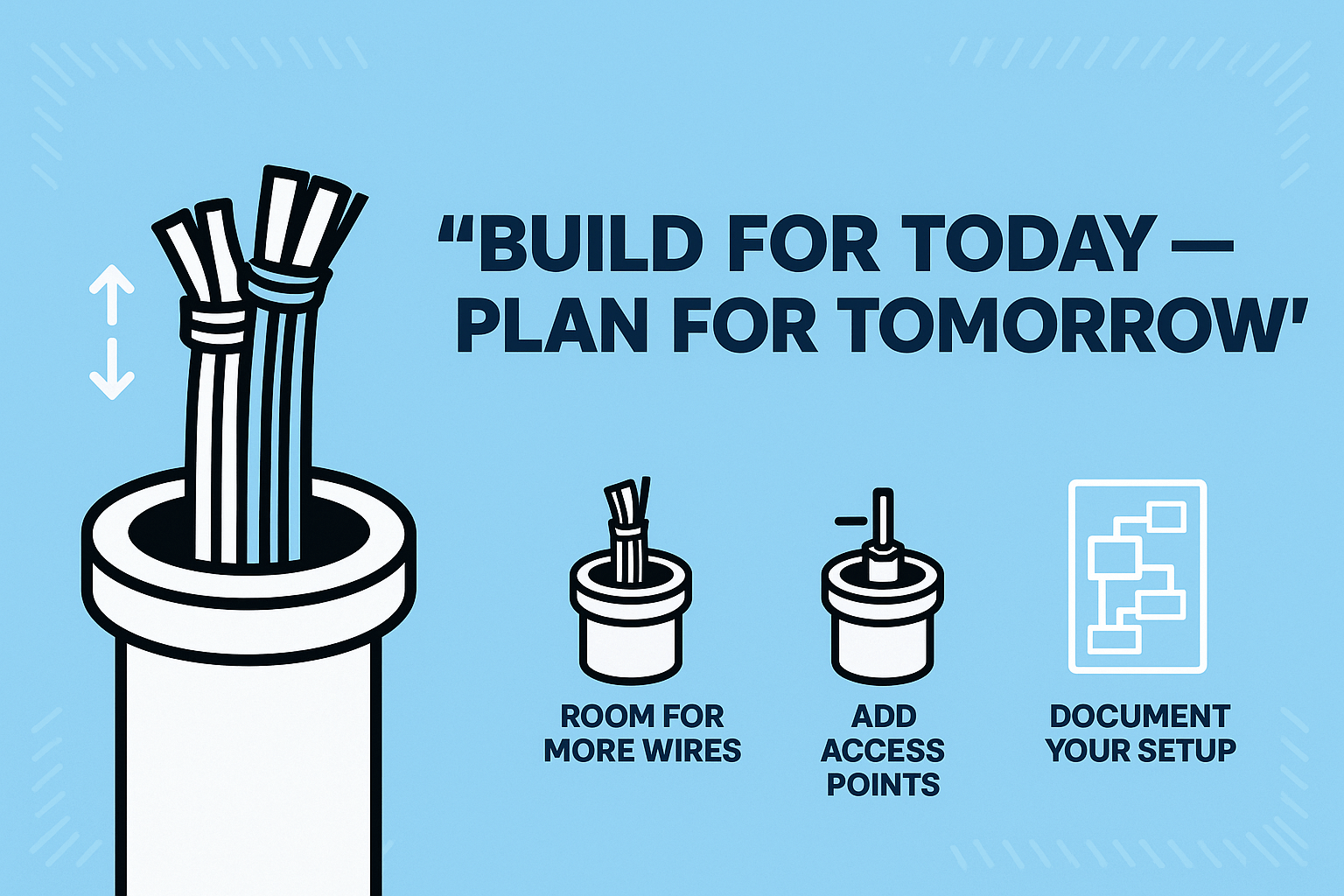
If your electrical system may need changes down the road — whether it’s adding circuits, upgrading equipment, or expanding into new areas — then conduit is almost always the better long-term choice.
In homes, this might include smart home upgrades, EV charger installations, or future solar connections. In commercial settings, it could mean changing layouts, adding office desks, or expanding network systems. With conduit, you don’t need to tear down walls or run new cable routes — you simply pull new wires through the existing path.
This level of flexibility can save significant time and cost in the future. For example, if you install conduit from your main panel to your attic or garage now, you’ll be ready for whatever comes next — whether it’s an air conditioning upgrade, a hot tub, or a data cable for a home office.
Even if you don’t use conduit everywhere, installing it in key routes (like between floors, or from the panel to exterior walls) can make a huge difference later on. Think of it as future-proofing your property — a small investment now that avoids bigger problems later.
In short, if your wiring needs might grow or change, conduit gives you room to grow without the mess.
6. الخاتمة
Understanding the difference between cable and conduit isn’t just about knowing how wires are installed — it’s about making the right decision for safety, budget, and long-term flexibility.
If you’re working on a typical home project in a dry, protected space, cable offers a quick, code-compliant solution that gets the job done with minimal effort. It’s affordable, simple, and widely used in residential construction for good reason.
But when wiring is exposed, runs underground, or needs to stand up to moisture or impact — or if you think your electrical system might need changes in the future — conduit becomes the better choice. It offers protection where it’s needed most and makes it easier to adapt down the road.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The best choice depends on the space, the environment, the level of protection required, and how much flexibility you want to build in. Whether you’re a homeowner planning a renovation or a professional managing a large installation, taking the time to understand your options can lead to smarter, safer, and more future-ready electrical systems.
If you’re unsure what to use in your project, don’t hesitate to consult your local code or talk to a licensed electrician — sometimes a quick conversation can save hours of guesswork and rework later.
كتوب is a company that provides high-quality electrical conduit products. We specialize in PVC, UPVC, and LSZH conduits, suitable for a wide range of electrical installations. Our products are certified to meet standards in different countries, giving you peace of mind for your projects.
Hope this article has been helpful to you—thanks for reading! Wishing you success with your project. If you have any related needs, feel free to contact us.
الأسئلة الشائعة
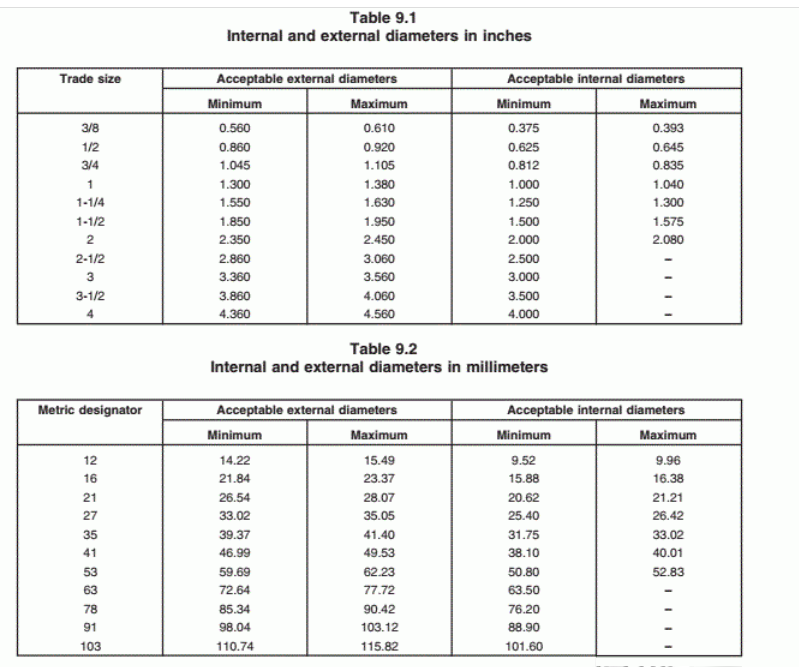
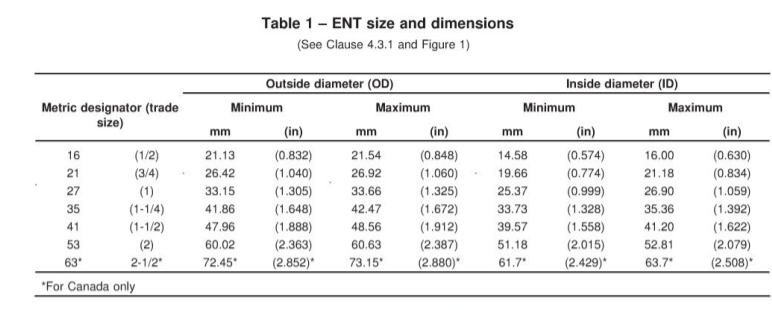
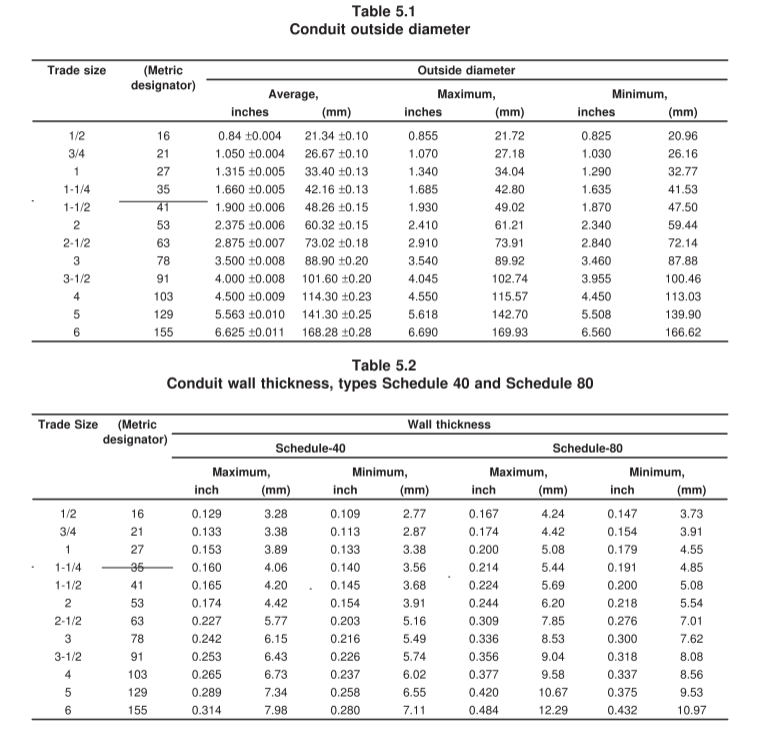
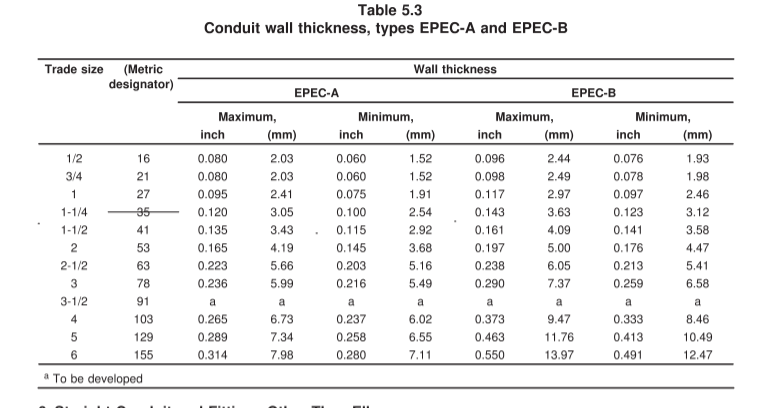
Q1. What size conduit do I need?
That depends on how many and what type of wires you’re running. Conduit fill calculations ensure the wires won’t overheat or be damaged. As a rule of thumb, never overfill conduit — and when in doubt, go one size up. For accurate sizing, use a conduit fill chart or consult an electrician.
Q2. Is conduit more expensive than cable?
Yes, generally speaking. Conduit systems are more expensive upfront due to additional materials (tubing, fittings) and labor (cutting, bending, pulling wires). However, conduit can reduce long-term costs by making future upgrades and maintenance easier — especially in commercial or complex installations.
Q3. Can I install conduit or cable myself, or do I need an electrician?
In some areas, homeowners can perform minor electrical work, including installing cable or conduit, as long as it meets local code and passes inspection. However, for safety and compliance — especially on commercial, outdoor, or high-voltage work — it’s always best to hire a licensed electrician.
What is the Difference Between Cables and Conduits اقرأ أكثر "